15+ Chinese Military Bases: A Visual Guide To Asia's Power
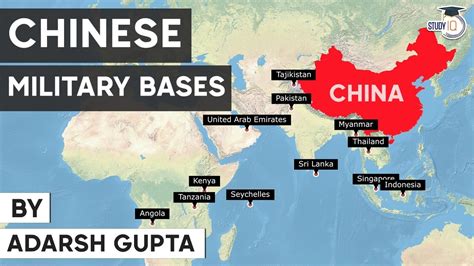
Introduction to China’s Military Presence in Asia

China’s military expansion in Asia has been a topic of growing interest and concern, as the country’s ambitious infrastructure projects and strategic initiatives have led to the establishment of numerous military bases across the region. This visual guide aims to provide an overview of China’s military presence, highlighting key locations and their significance. By exploring these bases, we can gain insights into China’s strategic goals and its role as a rising power in Asia.
1. Djibouti: A Strategic Foothold in the Horn of Africa

Djibouti, a small country in the Horn of Africa, hosts China’s first overseas military base, which became operational in 2017. This base serves as a crucial foothold for China’s military presence in the region. Located near the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait, a vital chokepoint for global trade, the base allows China to project power and protect its interests in the Indian Ocean and beyond.
2. Pakistan: A Long-Standing Alliance

China has maintained a strong military relationship with Pakistan for decades. The two countries have collaborated on various defense projects, and China has provided military assistance and training to Pakistan’s armed forces. While there are no official Chinese military bases in Pakistan, the close alliance and frequent military exercises highlight the strategic importance of this partnership.
3. Sri Lanka: Hambantota Port and Beyond

Sri Lanka has emerged as a key strategic location for China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI). The Hambantota Port, developed with Chinese investment, has raised concerns about its potential military use. Although China denies any military intentions, the port’s proximity to important shipping lanes and its deep-water capabilities make it a significant asset. Additionally, China has shown interest in developing other ports and infrastructure projects in Sri Lanka, further strengthening its presence.
4. Maldives: A Potential Strategic Hub
The Maldives, an archipelago in the Indian Ocean, has become a focus of China’s diplomatic and economic efforts. While no official military bases exist in the Maldives, China’s growing influence and investments have raised concerns. The country’s strategic location and the potential for establishing a military presence have led to speculations about China’s long-term plans.
5. Myanmar: A Complex Relationship

Myanmar, a Southeast Asian country, has a complex relationship with China. While the two nations have strong economic ties, political and security dynamics often influence their interactions. China has shown interest in developing infrastructure projects in Myanmar, including ports and special economic zones. The potential for military cooperation and access to Myanmar’s strategic locations remains a topic of discussion.
6. Cambodia: A New Frontier for Chinese Influence

Cambodia has emerged as a new frontier for Chinese influence in Southeast Asia. The country has welcomed Chinese investments and has shown willingness to align with China’s strategic interests. While no official military bases exist in Cambodia, the potential for military cooperation and the development of dual-use infrastructure has raised concerns among regional powers.
7. Thailand: A Balancing Act

Thailand, a regional power in Southeast Asia, maintains a delicate balance in its foreign relations. While China is a significant economic partner, Thailand also has strong ties with the United States and other regional players. China’s growing influence and its interest in developing infrastructure projects in Thailand have led to a cautious approach from the Thai government.
8. Laos: A Key Link in the Belt and Road Initiative

Laos, a landlocked country in Southeast Asia, plays a crucial role in China’s Belt and Road Initiative. The China-Laos Railway, a major infrastructure project, connects China’s southwestern provinces to Vientiane, the capital of Laos. This railway not only facilitates trade but also provides a potential military transportation route. The project’s strategic importance has raised concerns among neighboring countries.
9. Vietnam: A Historical Rivalry

Vietnam and China have a long history of rivalry and territorial disputes. Despite their shared communist ideology, the two countries have competing claims in the South China Sea. While no official Chinese military bases exist in Vietnam, the potential for military tensions and conflicts remains a concern. The South China Sea disputes and the balance of power in the region are key factors shaping China’s military strategy.
10. Philippines: A Shifting Dynamic
The Philippines, a Southeast Asian nation, has experienced a shifting dynamic in its relationship with China. The South China Sea disputes and the Philippines’ historical claims have led to tensions. However, recent years have seen a thaw in relations, with both countries seeking to improve ties. While no official Chinese military bases exist in the Philippines, the potential for future cooperation and the resolution of territorial disputes remain topics of discussion.
11. Indonesia: Navigating Geopolitical Challenges
Indonesia, the largest economy in Southeast Asia, faces unique geopolitical challenges. While maintaining a balanced foreign policy, Indonesia has to navigate its relationships with regional powers, including China. The potential for military cooperation and the development of strategic infrastructure have been topics of discussion between the two nations.
12. India: A Strategic Rivalry
India and China share a complex relationship marked by both cooperation and rivalry. The two countries have competing interests in the Indian Ocean and the Himalayas. The disputed border regions and the potential for military conflicts have led to a tense dynamic. While no official Chinese military bases exist in India, the strategic rivalry and the balance of power in the region are crucial factors shaping both countries’ military strategies.
13. Nepal: A Gateway to the Himalayas
Nepal, a landlocked country in South Asia, serves as a gateway to the Himalayas. China has shown interest in developing infrastructure projects in Nepal, including roads and railways, to enhance connectivity and trade. While no official military bases exist in Nepal, the potential for military cooperation and the strategic location of the country have raised discussions about China’s long-term plans.
14. Mongolia: A Unique Partnership
Mongolia, a landlocked country between China and Russia, has a unique partnership with China. The two countries have strong economic ties, and China is a major investor in Mongolia’s mining and infrastructure sectors. While no official military bases exist in Mongolia, the potential for military cooperation and the country’s strategic location have been topics of discussion.
15. Japan: A Historical Rivalry and a Modern Alliance
Japan and China have a long history of rivalry, dating back to World War II. However, in recent years, the two countries have sought to improve their relationship and strengthen economic ties. While no official Chinese military bases exist in Japan, the potential for military tensions and the balance of power in the region remain important considerations.
Visualizing China’s Military Presence

The above map provides a visual representation of China’s military bases and strategic locations across Asia. Each pin marks a significant site, allowing readers to grasp the extent and distribution of China’s military presence.
Conclusion
China’s military expansion in Asia is a complex and evolving dynamic. Through its strategic initiatives and infrastructure projects, China has established a significant presence across the region. From Djibouti to Indonesia, each base and location serves a unique purpose, reflecting China’s ambition to project power and protect its interests. As China continues to rise as a global power, its military presence in Asia will remain a topic of international interest and scrutiny.
FAQ
What is the significance of China’s military base in Djibouti?
+China’s military base in Djibouti provides a strategic foothold in the Horn of Africa, allowing China to protect its interests in the Indian Ocean and beyond. It is located near a vital chokepoint for global trade, enhancing China’s power projection capabilities.
How does China’s relationship with Pakistan impact its military presence in Asia?
+China’s strong military relationship with Pakistan provides an ally in the region. While no official bases exist, the close alliance and frequent military exercises highlight the strategic importance of this partnership, allowing China to extend its influence and protect its interests.
What are the concerns surrounding China’s involvement in Sri Lanka’s ports?
+China’s involvement in Sri Lanka’s ports, particularly Hambantota, has raised concerns about potential military use. The port’s deep-water capabilities and proximity to important shipping lanes make it a valuable asset, leading to speculations about China’s long-term strategic goals.
How does China’s influence in the Maldives impact the region’s security?
+China’s growing influence and investments in the Maldives have raised concerns among regional powers. The potential for establishing a military presence and the country’s strategic location could shift the balance of power, impacting regional security dynamics.
What are the key challenges in China’s relationship with Myanmar?
+China’s relationship with Myanmar is complex, influenced by political and security dynamics. While economic ties are strong, the potential for military cooperation and access to strategic locations remains a topic of discussion, shaping the balance of power in the region.

