17 Special Forces Test Requirements: Ultimate Guide To Selection
17 Special Forces Test Requirements: Ultimate Guide To Selection

The United States Army Special Forces, often referred to as the Green Berets, are an elite group of soldiers known for their exceptional skills and specialized training. Becoming a part of this renowned force is no easy feat, as the selection process is rigorous and demanding. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the 17 Special Forces Test Requirements, providing you with an in-depth understanding of what it takes to make it through this challenging journey.
Understanding the Special Forces Selection Process
The Special Forces selection process is designed to identify individuals with the physical, mental, and psychological attributes required to excel in this highly specialized unit. It is a multi-stage process that assesses various aspects of a candidate’s abilities and resilience. Let’s break down the key components of the selection process:
Initial Screening and Application: The journey begins with an initial screening process, where candidates must meet certain basic requirements. This includes being a U.S. citizen, holding a valid security clearance, and possessing a high school diploma or equivalent. Additionally, candidates must have a specific military occupational specialty (MOS) or a relevant civilian occupation.
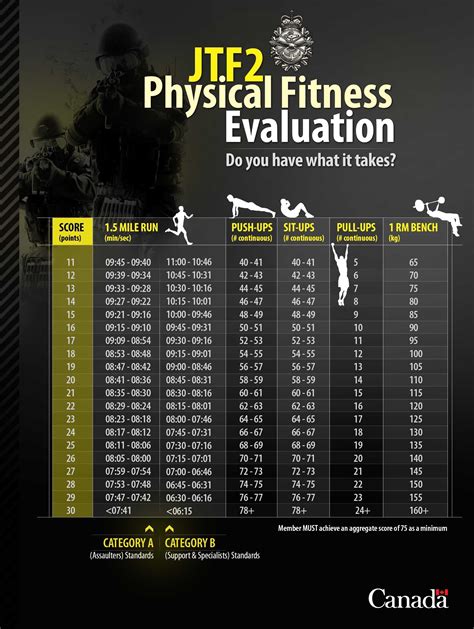
Physical Fitness Assessment: Physical fitness is a crucial aspect of Special Forces operations. Candidates must undergo a rigorous physical fitness assessment, which includes a battery of tests to evaluate their strength, endurance, and overall physical capabilities. This assessment is designed to push candidates to their limits and ensure they possess the necessary physical attributes for the demanding nature of Special Forces missions.
Psychological Evaluation: The Special Forces selection process places a strong emphasis on psychological resilience and mental toughness. Candidates undergo a comprehensive psychological evaluation to assess their ability to handle stress, make sound decisions under pressure, and maintain composure in high-stakes situations. This evaluation helps identify individuals with the mental fortitude required to thrive in the challenging environment of Special Forces operations.
Medical Examination: A thorough medical examination is conducted to ensure candidates are in optimal health and free from any physical limitations that may hinder their performance. This examination assesses various aspects of physical health, including cardiovascular fitness, musculoskeletal strength, and overall well-being. Any medical conditions or injuries that could impact a candidate’s ability to perform Special Forces duties are carefully evaluated.
Special Forces Assessment and Selection (SFAS): SFAS is the heart of the selection process, where candidates are put through a series of demanding physical and mental challenges. This phase is designed to simulate the rigors of Special Forces training and operations. Candidates must demonstrate their ability to perform under extreme conditions, navigate complex terrain, and execute specialized tasks. SFAS is a true test of a candidate’s physical and mental resilience, teamwork, and leadership skills.
Language Proficiency: The Special Forces operate in diverse environments, often requiring communication with local populations and allies. As such, language proficiency is a crucial aspect of the selection process. Candidates are assessed on their ability to communicate in a foreign language, with a focus on languages relevant to potential deployment areas. Proficiency in a foreign language enhances a candidate’s value and increases their chances of selection.
Specialty Training: Once candidates have successfully completed the SFAS phase, they enter into specialized training tailored to their specific role within the Special Forces. This training is highly intensive and focuses on developing advanced skills in areas such as combat diving, parachute operations, and specialized weaponry. Candidates must master these skills to become fully operational Special Forces soldiers.
The 17 Special Forces Test Requirements
Now, let’s dive into the 17 specific test requirements that candidates must meet to progress through the Special Forces selection process:
Physical Fitness Test (PFT): The PFT is a critical component of the selection process, assessing a candidate’s overall physical fitness. It consists of various exercises, including push-ups, sit-ups, pull-ups, and a timed 2-mile run. Candidates must achieve a minimum score in each event to progress to the next stage.
Swimming Test: Candidates must demonstrate their swimming proficiency by completing a 500-yard swim in a specified time. This test evaluates their ability to navigate through water, an essential skill for many Special Forces operations.
Land Navigation Test: Land navigation is a crucial skill for Special Forces soldiers, as they often operate in unfamiliar terrain. Candidates must navigate through a complex course, using map and compass skills to reach designated points within a specified time frame.
Rucksack March: The rucksack march is a challenging endurance test, where candidates must carry a heavy rucksack (backpack) and march a specified distance within a given time. This test assesses their ability to endure physical hardship and maintain forward momentum.
Obstacle Course: The obstacle course is designed to test a candidate’s agility, balance, and physical strength. It consists of various obstacles, such as walls, ropes, and cargo nets, that candidates must navigate through in a timely manner.
Weapon Proficiency: Candidates must demonstrate proficiency with various weapons systems, including pistols, rifles, and machine guns. They are evaluated on their accuracy, speed, and tactical understanding during live-fire exercises.
Explosive Hazardous Material (EHM) Handling: Special Forces soldiers often encounter explosive and hazardous materials in their operations. Candidates must undergo training and evaluation on proper handling and disposal procedures to ensure their safety and the safety of their teammates.
Combat Diver Qualification: For certain Special Forces roles, candidates must undergo combat diver qualification training. This training teaches them underwater navigation, breathing techniques, and specialized equipment handling, enabling them to operate effectively in aquatic environments.
Parachute Operations: Parachute operations are a fundamental skill for Special Forces soldiers. Candidates must complete a series of jumps, including static line and freefall jumps, to demonstrate their proficiency in this critical area.
Language Proficiency Test: As mentioned earlier, language proficiency is a key requirement for Special Forces soldiers. Candidates must pass a language proficiency test in a foreign language, demonstrating their ability to communicate effectively in a second language.
Specialty Skill Assessment: Depending on the specific role within the Special Forces, candidates may be required to undergo additional specialty skill assessments. These assessments evaluate their expertise in areas such as medical skills, engineering, or intelligence gathering.
Leadership and Teamwork Evaluation: Throughout the selection process, candidates are closely observed for their leadership and teamwork abilities. They must demonstrate effective communication, decision-making, and the ability to work cohesively within a team. Leadership potential is a critical factor in the selection of Special Forces soldiers.
Physical Resilience and Stamina: The Special Forces operate in some of the most challenging environments on Earth. Candidates must possess exceptional physical resilience and stamina to endure long missions, extreme weather conditions, and intense physical demands.
Mental Fortitude and Stress Management: The psychological demands of Special Forces operations are immense. Candidates must showcase their ability to remain calm under pressure, make sound decisions, and effectively manage stress. Mental fortitude is a key differentiator between those who make it through the selection process and those who do not.
Adaptability and Creativity: Special Forces soldiers often face unpredictable situations and must adapt quickly to changing circumstances. Candidates are evaluated on their ability to think creatively, problem-solve, and find innovative solutions to complex challenges.
Ethical Decision-Making: The Special Forces operate under strict ethical guidelines and principles. Candidates must demonstrate their understanding of these principles and their ability to make ethical decisions in high-pressure situations. Integrity and moral courage are essential traits for Special Forces soldiers.
Cultural Awareness and Sensitivity: As Special Forces soldiers frequently interact with diverse populations, cultural awareness and sensitivity are crucial. Candidates are assessed on their understanding of cultural norms, customs, and protocols, ensuring they can effectively engage with local communities and build trust.
Physical and Mental Endurance: The selection process is designed to push candidates to their limits, both physically and mentally. Those who succeed must possess exceptional endurance, both in terms of physical stamina and mental resilience. They must be able to persevere through fatigue, pain, and adversity.
Tips for Success in the Special Forces Selection Process
Now that we have covered the 17 test requirements, let’s explore some key strategies and tips to help you excel in the Special Forces selection process:
Physical Preparation: Prioritize physical fitness and conditioning. Develop a well-rounded training regimen that focuses on strength, endurance, and cardiovascular fitness. Aim to exceed the minimum requirements in each physical fitness assessment.
Mental Toughness: Build mental resilience by exposing yourself to challenging situations and pushing through mental barriers. Practice stress management techniques, such as meditation or visualization, to enhance your ability to remain calm and focused under pressure.
Specialty Skills: If you have a specific skill set that aligns with a Special Forces role, such as medical expertise or engineering, invest time in developing and refining those skills. Special Forces value individuals with specialized abilities that contribute to the team’s overall effectiveness.
Study and Research: Familiarize yourself with the Special Forces selection process, including the test requirements and evaluation criteria. Research past experiences and success stories to gain insights into what is expected of candidates. Study relevant military manuals and guidelines to enhance your understanding of Special Forces operations.
Practice and Repetition: Practice makes perfect. Rehearse the various tests and assessments that you will encounter during the selection process. Find study groups or training partners who can provide feedback and support. Repetition will help you refine your skills and improve your performance.
Nutrition and Rest: Proper nutrition and adequate rest are essential for optimal performance. Ensure you are fueling your body with a balanced diet and getting sufficient sleep to support your physical and mental recovery.
Stay Motivated: The selection process can be demanding and challenging. Stay motivated by reminding yourself of your goals and the impact you want to make as a Special Forces soldier. Surround yourself with a supportive network of friends and family who can provide encouragement and accountability.
Seek Professional Guidance: Consider seeking guidance from experienced Special Forces soldiers or selection trainers. They can provide valuable insights, mentorship, and personalized advice to help you navigate the selection process effectively.
Conclusion
The journey to becoming a part of the United States Army Special Forces is an extraordinary one, filled with challenges and opportunities for personal growth. By understanding the 17 Special Forces Test Requirements and implementing the strategies outlined in this guide, you can increase your chances of success in the selection process. Remember, the Special Forces seek individuals who possess a unique combination of physical prowess, mental fortitude, and specialized skills. Embrace the challenge, push your limits, and embrace the honor of serving in one of the most elite military units in the world.
🌟 Note: This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the Special Forces selection process and test requirements. For the most up-to-date and detailed information, always refer to official military sources and consult with experienced Special Forces personnel.
What is the average age of Special Forces soldiers?
+The average age of Special Forces soldiers can vary, but it is typically between 25 and 35 years old. However, there are no strict age restrictions, and individuals who demonstrate exceptional skills and meet the physical and mental requirements can be considered for selection regardless of their age.
Can civilians apply for the Special Forces?
+Yes, civilians can apply for the Special Forces. However, they must first enlist in the U.S. Army and meet the basic eligibility requirements. Civilian applicants undergo the same rigorous selection process as military personnel.
How long does the Special Forces selection process take?
+The Special Forces selection process can vary in duration, but it typically takes several months to complete. The process includes various stages, such as initial screening, physical fitness assessment, psychological evaluation, and the Special Forces Assessment and Selection (SFAS) phase. Each stage has its own timeline and requirements.
What are the physical fitness requirements for Special Forces selection?
+The physical fitness requirements for Special Forces selection are rigorous and demanding. Candidates must meet minimum standards in various exercises, including push-ups, sit-ups, pull-ups, and a timed 2-mile run. The exact requirements can vary, so it is important to refer to official military sources for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
What happens after successful completion of the Special Forces selection process?
+Upon successful completion of the Special Forces selection process, candidates are assigned to a specific Special Forces unit and undergo further specialized training. This training focuses on developing advanced skills and knowledge specific to their role within the unit. Once training is complete, they become fully operational Special Forces soldiers, ready to deploy and execute missions.


