2 Force Member

Introduction to 2 Force Members

In the realm of physics and engineering, understanding the concept of forces is crucial for analyzing and designing systems. A 2 force member refers to a structural element that is subjected to only two forces. This concept is fundamental in the study of mechanics of materials and is used extensively in the design of machines, buildings, and bridges.
📝 Note: The study of forces and their effects on different types of members is essential for ensuring the stability and safety of structures.
Types of 2 Force Members
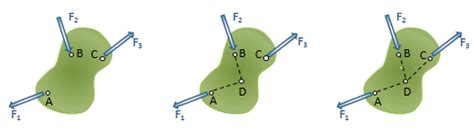
There are primarily two types of 2 force members: - Tension members: These are structural elements that are subjected to tensile forces, meaning they are being pulled apart. Examples include cables, ropes, and chains. - Compression members: These elements are subjected to compressive forces, meaning they are being squeezed. Examples include columns and pillars.
Characteristics of 2 Force Members

2 force members have several distinct characteristics: - They are subjected to only two forces, which are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. - The forces act along the longitudinal axis of the member. - The member is either in tension or compression. - The cross-sectional area of the member remains constant along its length.
Advantages of 2 Force Members
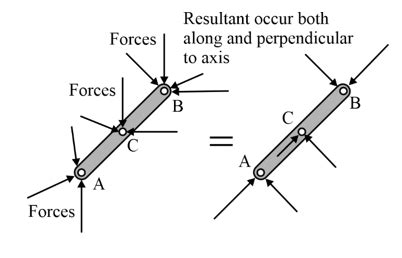
The use of 2 force members in structural design offers several advantages, including: - Simpllicity: The analysis and design of 2 force members are relatively straightforward. - Efficiency: 2 force members can be designed to be very efficient in terms of material usage. - Cost-effectiveness: The simplicity and efficiency of 2 force members can result in cost savings.
Applications of 2 Force Members
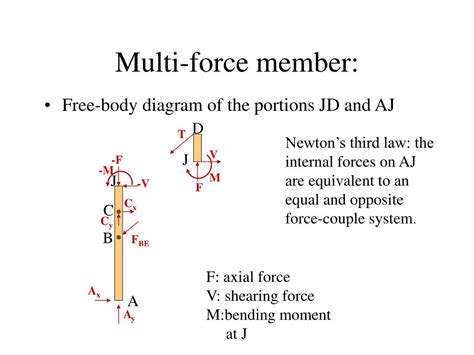
2 force members are used in a wide range of applications, including: - Building design: Columns, beams, and roof trusses often consist of 2 force members. - Bridge design: Cables, suspender cables, and main cables in suspension bridges are examples of 2 force members. - Machine design: Links, rods, and cables in machines are often designed as 2 force members.
Analysis of 2 Force Members

The analysis of 2 force members involves determining the forces acting on the member and the resulting stresses and strains. This can be done using various methods, including: - Free body diagrams: A graphical representation of the forces acting on a member. - Equilibrium equations: Mathematical equations that describe the balance of forces acting on a member.
| Type of Member | Force | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Tension member | Tensile force | Cable |
| Compression member | Compressive force | Column |
Design Considerations
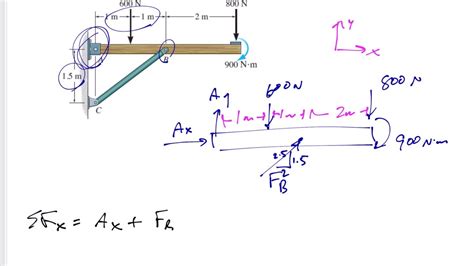
When designing 2 force members, several factors must be considered, including: - Material properties: The strength, stiffness, and ductility of the material. - Load conditions: The magnitude and type of loads acting on the member. - Geometric constraints: The length, cross-sectional area, and shape of the member.
📝 Note: The design of 2 force members requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure safety and efficiency.
In summary, 2 force members play a crucial role in the design of various structures and machines. Understanding the characteristics, advantages, and applications of 2 force members is essential for engineers and designers. By considering the various design factors and using appropriate analysis methods, 2 force members can be designed to be safe, efficient, and cost-effective.
What are the types of 2 force members?
+
The two primary types of 2 force members are tension members and compression members.
What are the advantages of using 2 force members?
+
The advantages of using 2 force members include simplicity, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
What are some common applications of 2 force members?
+
2 force members are commonly used in building design, bridge design, and machine design.


