Are Deer Nocturnal

Introduction to Deer Behavior

Deer are fascinating creatures that inhabit various parts of the world, and their behavior has been a subject of interest for many wildlife enthusiasts and researchers. One question that often arises is whether deer are nocturnal, meaning they are most active at night. To answer this question, we need to delve into the habits and patterns of deer and explore their activity levels throughout the day.
Understanding Deer Activity Patterns

Deer are known to be crepuscular animals, which means they are most active during twilight hours, i.e., dawn and dusk. This is the time when they tend to feed, mate, and engage in other activities. However, their activity patterns can vary depending on the species, habitat, and other environmental factors. For example, white-tailed deer are more active during the night in areas with high human activity, while mule deer tend to be more diurnal, meaning they are active during the day.
Factors Influencing Deer Activity

Several factors can influence deer activity patterns, including: * Food availability: Deer tend to be more active during times when food is readily available. * Predator avoidance: Deer may adjust their activity patterns to avoid predators, such as coyotes, mountain lions, or humans. * Weather conditions: Deer may be more active during mild weather conditions and less active during extreme temperatures or precipitation. * Breeding season: Deer may be more active during the breeding season, which typically occurs in the fall.
Are Deer Nocturnal?
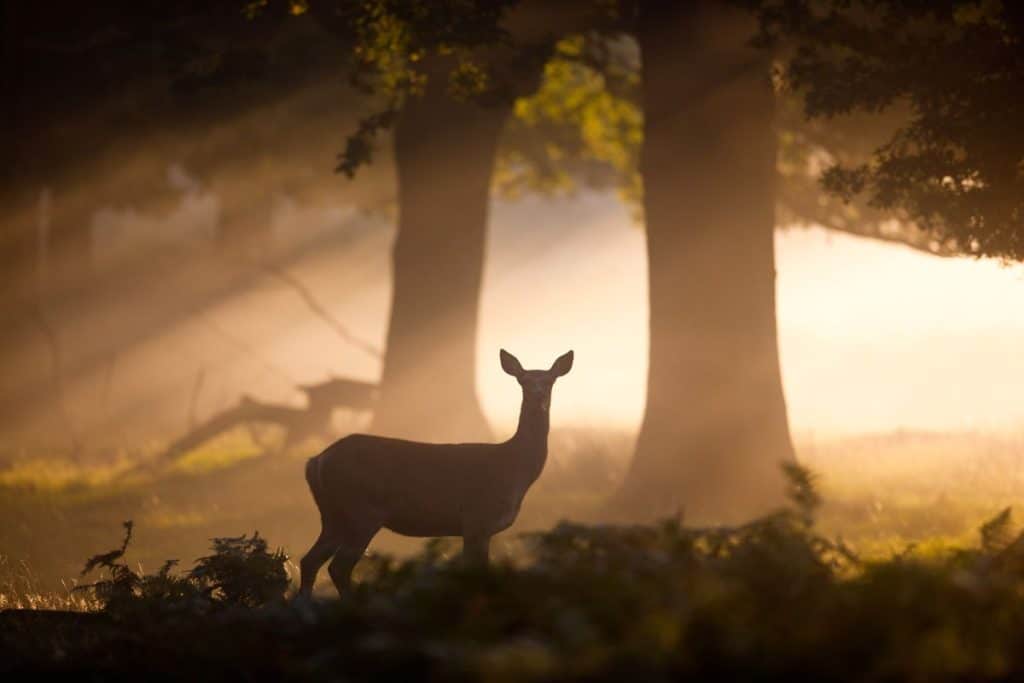

While deer are not strictly nocturnal, they do exhibit some nocturnal behavior, particularly in areas with high human activity or when they feel threatened. However, their crepuscular nature means they are most active during twilight hours, and their activity levels can vary throughout the day. In fact, some studies have shown that deer can be active during all hours of the day, although their activity peaks during dawn and dusk.
Deer Behavior at Night

At night, deer tend to: * Rest and hide: Deer often bed down in dense vegetation or under cover to rest and hide from predators. * Feed: Deer may feed at night, particularly in areas with abundant food sources. * Travel: Deer may travel at night, especially during the breeding season or when migrating between summer and winter habitats.
🦌 Note: Deer behavior can vary significantly depending on the species, habitat, and environmental factors, so it's essential to consider these factors when understanding deer activity patterns.
Observing Deer in the Wild

If you’re interested in observing deer in the wild, consider the following tips: * Be patient: Deer can be elusive, so be prepared to spend time waiting and observing. * Choose the right location: Look for areas with abundant food sources and suitable habitat. * Use binoculars: Binoculars can help you spot deer from a distance without disturbing them.
| Deer Species | Activity Pattern |
|---|---|
| White-tailed deer | Crepuscular, with some nocturnal behavior |
| Mule deer | Diurnal, with some crepuscular behavior |
| Red deer | Crepuscular, with some nocturnal behavior |

In summary, deer are not strictly nocturnal, but they do exhibit some nocturnal behavior, particularly in areas with high human activity or when they feel threatened. Their crepuscular nature means they are most active during twilight hours, and their activity levels can vary throughout the day. By understanding deer behavior and activity patterns, we can better appreciate these fascinating creatures and their importance in ecosystems around the world.
What is the best time to observe deer in the wild?
+
The best time to observe deer in the wild is during twilight hours, i.e., dawn and dusk, when they are most active.
Do deer sleep at night?
+
Deer do rest and hide at night, but they do not sleep in the same way that humans do. They often take short naps and can wake up quickly if needed.
Can deer see in the dark?
+
Deer have relatively poor eyesight in low light conditions, but their senses of smell and hearing are highly developed, which helps them navigate and detect predators at night.