Army Cyber Security Jobs

Introduction to Army Cyber Security Jobs

The US Army has been at the forefront of cyber security efforts, recognizing the critical role that cyber defense plays in national security. As technology advances and the threat landscape evolves, the demand for skilled cyber security professionals in the Army has never been higher. Army cyber security jobs are diverse, ranging from cyber operations to intelligence analysis, and offer a unique opportunity for individuals to serve their country while developing valuable skills in a rapidly growing field.
Cyber Security Career Paths in the Army
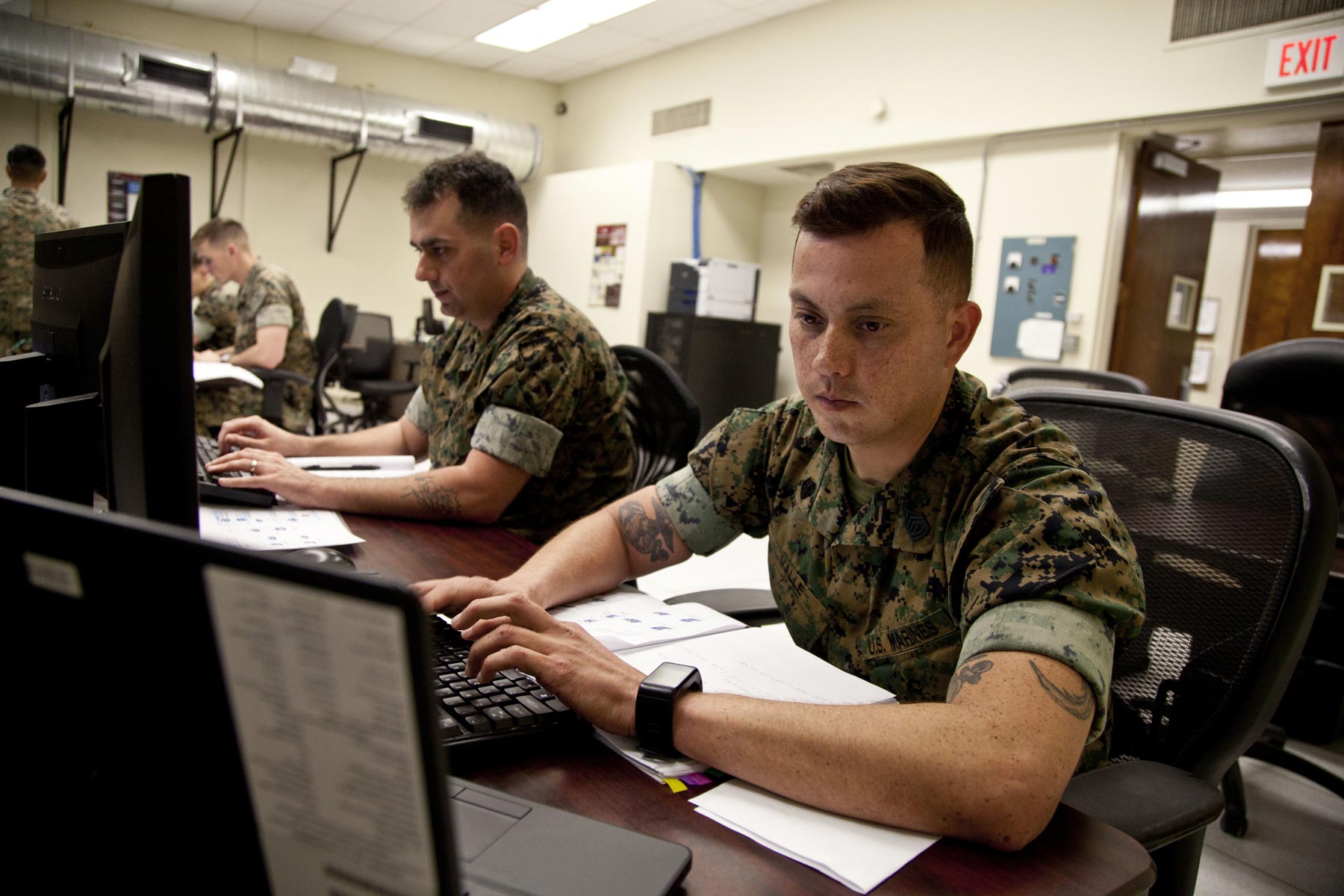

The Army offers a variety of career paths for those interested in cyber security, including: - Cyber Operations Specialist: Responsible for conducting cyber operations across the full spectrum of conflict, from defensive to offensive operations. - Intelligence Analyst: Works to analyze and interpret cyber intelligence to support Army operations and decision-making. - Cyber Security Specialist: Focuses on protecting Army networks and systems from cyber threats, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of critical information. - Network Operations Specialist: Manages and maintains Army communication networks, ensuring they remain secure and operational. - Information Assurance Specialist: Develops and implements information assurance policies and procedures to protect Army information systems.
These roles are not only crucial for the Army’s cyber security posture but also provide servicemembers with in-demand skills that are highly valued in the civilian job market.
Requirements and Training for Army Cyber Security Jobs

To be eligible for Army cyber security jobs, individuals typically need to meet certain education and skill requirements, including: - Holding a high school diploma or equivalent - Scoring well on the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test, particularly in areas related to electronics and mechanics - Completing basic training and then attending Advanced Individual Training (AIT) for their specific job specialty - Obtaining security clearances, which may require background checks and screenings
The Army also provides ongoing training and education in cyber security, including certifications and advanced degrees, to ensure that servicemembers stay up-to-date with the latest technologies and threats.
Benefits of Army Cyber Security Careers
A career in Army cyber security offers numerous benefits, including: - Job security and stability - Opportunities for advancement - Comprehensive benefits package, including health insurance, retirement plans, and education assistance - Chance to serve a higher purpose and contribute to national security - Development of highly marketable skills in a growing field
For those interested in a challenging and rewarding career that combines technology, national service, and personal growth, Army cyber security jobs are an attractive option.
Challenges in Army Cyber Security
While a career in Army cyber security can be highly rewarding, it also presents challenges, such as: - Constant evolution of threats: The cyber threat landscape is continually changing, requiring cyber security professionals to stay vigilant and adaptable. - High stress levels: The nature of cyber security work can be high-pressure, especially during times of crisis or when dealing with sophisticated threats. - Continuous learning: The rapid pace of technological change means that cyber security professionals must commit to lifelong learning to remain effective.
Despite these challenges, many find the rewards of a career in Army cyber security to outweigh the difficulties, offering a sense of purpose and fulfillment that is hard to find in other fields.
💡 Note: Individuals considering a career in Army cyber security should be prepared for the unique demands and challenges of this field, including the need for continuous learning and the potential for high-stress situations.
Future of Army Cyber Security

The future of Army cyber security is dynamic and evolving, with emerging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and cloud computing set to play increasingly important roles. As the Army continues to invest in cyber capabilities and digital transformation, the demand for skilled cyber security professionals will only continue to grow. This presents a significant opportunity for those interested in cyber security to make a meaningful contribution to national defense while being at the forefront of technological innovation.
| Cyber Security Role | Description | Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Cyber Operations Specialist | Conducts cyber operations | Basic training, AIT, security clearance |
| Intelligence Analyst | Analyzes cyber intelligence | Basic training, AIT, security clearance |
| Cyber Security Specialist | Protects Army networks and systems | Basic training, AIT, security clearance |

As the US Army continues to adapt to the evolving cyber security landscape, it is clear that careers in this field will remain vital to national security. For individuals with a passion for technology, a commitment to service, and a desire to be part of a dynamic and challenging field, Army cyber security jobs offer a unique and rewarding opportunity.
In essence, a career in Army cyber security is not just about protecting networks and systems; it’s about serving a critical role in national defense, developing highly sought-after skills, and being part of a community that is at the forefront of technological innovation and advancement. Whether one is just starting their career or looking for a new challenge, the Army’s cyber security field has much to offer, from the opportunity to make a real difference in national security to the chance to be part of a prestigious and elite group of cyber security professionals.
What are the primary roles in Army cyber security?
+The primary roles include Cyber Operations Specialist, Intelligence Analyst, Cyber Security Specialist, and Network Operations Specialist, among others.
What kind of training does the Army provide for cyber security careers?
+The Army provides basic training, Advanced Individual Training (AIT), and ongoing education and certifications to ensure that servicemembers have the skills needed to succeed in cyber security roles.
What are the benefits of pursuing a career in Army cyber security?
+Benefits include job security, opportunities for advancement, comprehensive benefits, the chance to serve a higher purpose, and the development of highly marketable skills.

