Army Field Medic Requirements
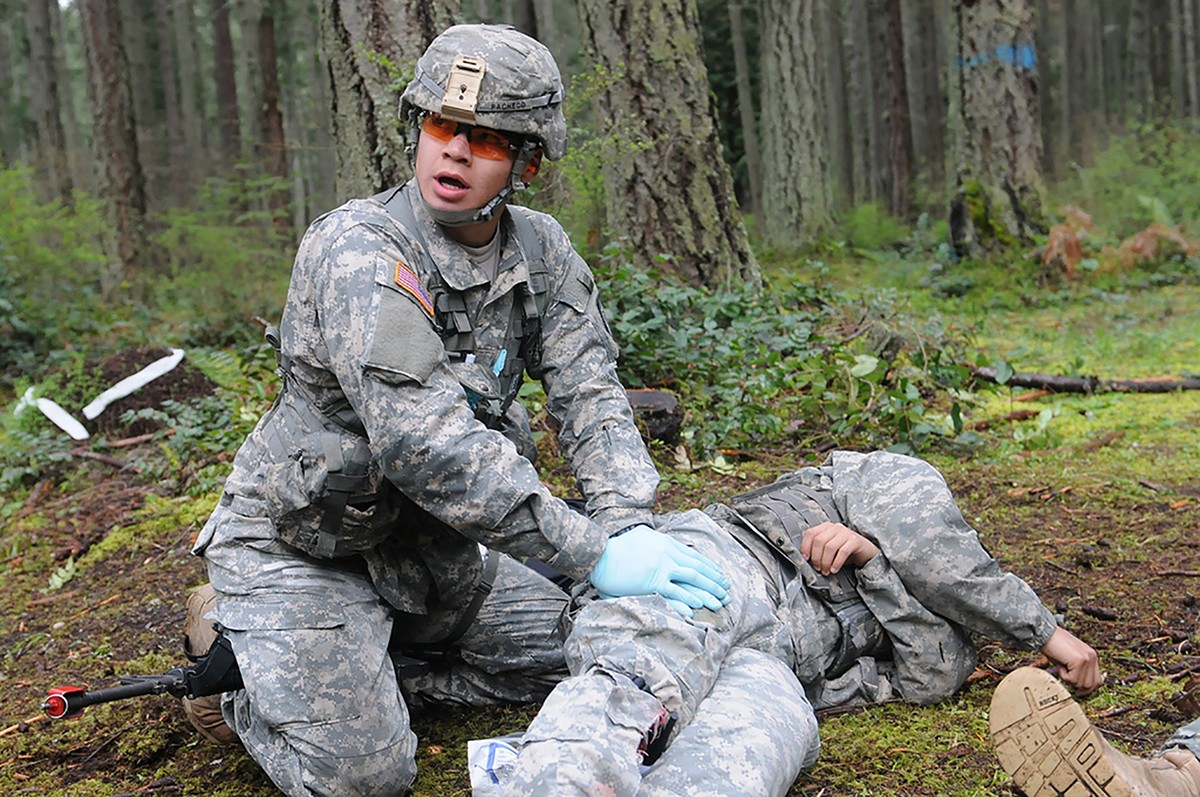

Introduction to Army Field Medic Requirements

The role of an Army Field Medic is crucial in providing medical care to soldiers in combat zones. These individuals are trained to administer emergency medical treatment, stabilize patients, and evacuate them to medical facilities for further care. To become an Army Field Medic, one must meet specific requirements and undergo rigorous training. In this article, we will explore the necessary qualifications, training, and skills required to become an Army Field Medic.
Basic Requirements

To be eligible for the Army Field Medic program, candidates must meet the following basic requirements: * Be a U.S. citizen * Be between the ages of 17 and 35 * Have a high school diploma or equivalent * Score well on the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) test * Pass a physical fitness test * Meet the medical standards set by the U.S. Army
Training and Education

Army Field Medics undergo extensive training to prepare them for the challenges of providing medical care in combat zones. The training program includes: * Basic Combat Training (BCT): This 10-week course teaches soldiers the fundamental skills needed to survive in combat, including first aid, combat tactics, and survival techniques. * Advanced Individual Training (AIT): This 16-week course provides specialized training in medical skills, including patient assessment, trauma care, and pharmacology. * Combat Medic Specialist Course: This 16-week course teaches soldiers advanced medical skills, including surgical techniques, patient evacuation, and medical logistics. * Continuous education and training: Army Field Medics are required to complete regular training and certification courses to stay up-to-date with the latest medical techniques and technologies.
Skills and Qualifications

Army Field Medics must possess a range of skills and qualifications, including: * Strong communication and interpersonal skills: The ability to communicate effectively with patients, colleagues, and commanders is critical in high-stress situations. * Physical stamina and endurance: Army Field Medics must be able to work in challenging environments, including extreme temperatures, rugged terrain, and combat zones. * Attention to detail and ability to work under pressure: Medics must be able to assess patients quickly and accurately, make sound judgments, and provide effective treatment in emergency situations. * Ability to work independently and as part of a team: Army Field Medics often work in small teams or alone, and must be able to make decisions and take action independently.
Certifications and Specializations
Army Field Medics can pursue various certifications and specializations, including: * Emergency Medical Technician (EMT) certification: This certification demonstrates a medic’s ability to provide emergency medical care, including patient assessment, trauma care, and medical transportation. * Tactical Combat Casualty Care (TCCC) certification: This certification teaches medics the skills needed to provide medical care in combat zones, including hemorrhage control, airway management, and patient evacuation. * Specialized medical training: Army Field Medics can receive training in specialized areas, such as surgical techniques, medical logistics, and patient administration.
👨⚕️ Note: Army Field Medics must also maintain their certification and training through regular continuing education courses and practice.
Deployment and Career Opportunities

Army Field Medics can be deployed to various locations, including combat zones, humanitarian missions, and disaster response situations. Career opportunities for Army Field Medics include: * Combat medic: Providing medical care to soldiers in combat zones. * Medical instructor: Teaching medical skills to other soldiers. * Medical logistics specialist: Coordinating medical supplies and equipment. * Medical administrator: Managing medical facilities and personnel.
| Rank | Job Description | Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Private (PVT) | Combat medic | Basic training, AIT, and combat medic specialist course |
| Sergeant (SGT) | Medical instructor | Basic training, AIT, combat medic specialist course, and instructor training |
| Staff Sergeant (SSG) | Medical logistics specialist | Basic training, AIT, combat medic specialist course, and logistics training |

In summary, becoming an Army Field Medic requires a combination of education, training, and skills. These individuals play a critical role in providing medical care to soldiers in combat zones, and their work is essential to the success of military operations. With various career opportunities and specializations available, Army Field Medics can build a rewarding and challenging career in the military.
What are the basic requirements to become an Army Field Medic?
+
To become an Army Field Medic, candidates must be a U.S. citizen, between the ages of 17 and 35, have a high school diploma or equivalent, score well on the ASVAB test, pass a physical fitness test, and meet the medical standards set by the U.S. Army.
What kind of training do Army Field Medics receive?
+
Army Field Medics undergo Basic Combat Training, Advanced Individual Training, and the Combat Medic Specialist Course. They also receive continuous education and training to stay up-to-date with the latest medical techniques and technologies.
What are the career opportunities for Army Field Medics?
+
Army Field Medics can pursue various career opportunities, including combat medic, medical instructor, medical logistics specialist, and medical administrator. They can also specialize in areas such as surgical techniques, medical logistics, and patient administration.

