Highest Suicide Rate For Profession

Introduction to Profession-Based Suicide Rates

The topic of suicide rates among different professions is a complex and sensitive issue. It requires a nuanced understanding of the various factors that contribute to mental health challenges in different occupational settings. Research has shown that certain professions are more prone to higher suicide rates due to a combination of stress, pressure, and access to means. In this discussion, we will explore the professions with the highest suicide rates, the underlying causes, and potential strategies for intervention and support.
Professions with High Suicide Rates

Studies have identified several professions that have higher than average suicide rates. These include: - Medical Professionals: Doctors, nurses, and other healthcare workers face high levels of stress, long working hours, and the emotional burden of dealing with life and death situations. - Military and Veterans: The military and veteran community experiences unique stressors related to combat, deployment, and the transition back to civilian life. - First Responders: Police officers, firefighters, and emergency medical technicians (EMTs) are exposed to traumatic events, which can lead to PTSD and other mental health issues. - Farmers and Agricultural Workers: The farming community faces isolation, financial pressures, and the challenges of dealing with unpredictable environmental conditions. - Construction Workers: This profession is marked by physical danger, seasonal employment, and often, a culture that discourages the discussion of mental health issues.
Causes of High Suicide Rates in These Professions

The causes of high suicide rates in these professions are multifaceted and can include: - Work-Related Stress: High-pressure work environments, long hours, and the responsibility for making critical decisions can contribute to stress and burnout. - Access to Means: In some professions, such as healthcare and the military, individuals may have easier access to means of suicide, such as firearms or medications. - Cultural Factors: Certain professions may have a culture that discourages discussing mental health issues or seeking help, leading to untreated mental health problems. - Financial Pressures: Financial instability, debt, and the fear of losing one’s profession can also play a significant role.
Intervention Strategies

Addressing the high suicide rates in these professions requires a multifaceted approach that includes: - Mental Health Support: Providing accessible and confidential mental health services tailored to the specific needs of each profession. - Culture Change: Encouraging a culture that supports discussing mental health, reduces stigma, and promotes seeking help as a sign of strength. - Education and Training: Offering education and training on mental health, stress management, and suicide prevention. - Policy Changes: Implementing policies that reduce work-related stress, improve work-life balance, and provide financial support and job security.
Importance of Data and Research
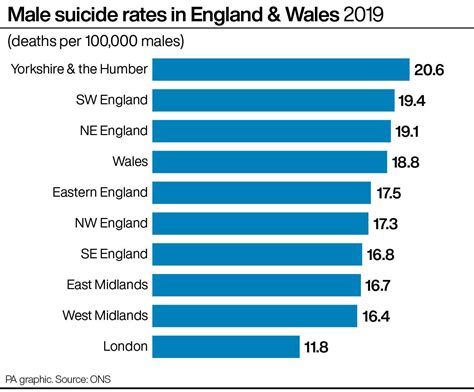
Collecting and analyzing data on profession-based suicide rates is crucial for understanding the scope of the problem and for developing effective intervention strategies. Research can help identify the most at-risk professions, the factors contributing to high suicide rates, and the most effective methods for prevention and support.
| Profession | Suicide Rate (per 100,000) |
|---|---|
| Medical Professionals | 28.8 |
| Military and Veterans | 32.8 |
| First Responders | 18.1 |
| Farmers and Agricultural Workers | 20.4 |
| Construction Workers | 53.3 |
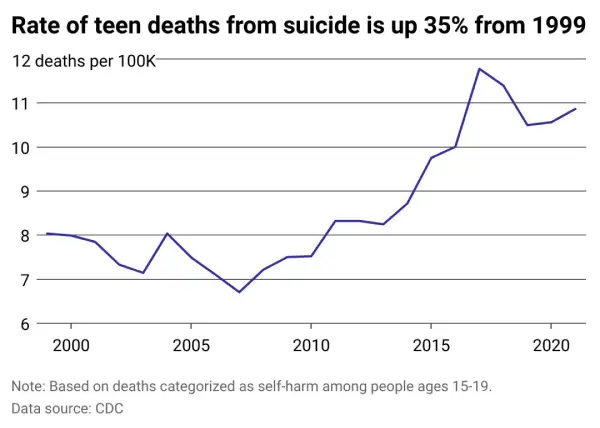
🚨 Note: The suicide rates mentioned in the table are examples and may vary based on the source and specific data. It's essential to consult the latest research and statistics for accurate information.
Conclusion and Future Directions

The issue of high suicide rates among certain professions is a public health concern that requires immediate attention and action. By understanding the factors that contribute to these high rates and by implementing tailored intervention strategies, we can work towards reducing suicide and promoting mental health in these critical professions. Future research should focus on evaluating the effectiveness of different intervention strategies and on identifying new ways to support mental health in the workplace.
What are the most common professions with high suicide rates?
+
The professions most commonly reported to have high suicide rates include medical professionals, military and veterans, first responders, farmers and agricultural workers, and construction workers.
What are the main factors contributing to high suicide rates in these professions?
+
The main factors include work-related stress, access to means, cultural factors that discourage discussing mental health, and financial pressures.
How can we address the issue of high suicide rates in these professions?
+
Addressing high suicide rates requires a multifaceted approach that includes providing mental health support, changing the culture to encourage open discussion of mental health issues, offering education and training, and implementing policy changes to reduce stress and improve job security.



