Military Ranks In The Navy
Introduction to Naval Hierarchy

The naval forces of any country are organized into a strict hierarchy, with each rank having its own set of responsibilities and duties. The ranks in the navy are designed to provide a clear chain of command, ensuring that orders are followed and missions are carried out efficiently. Understanding these ranks is essential for anyone interested in joining the navy or for those who want to learn more about the naval hierarchy.
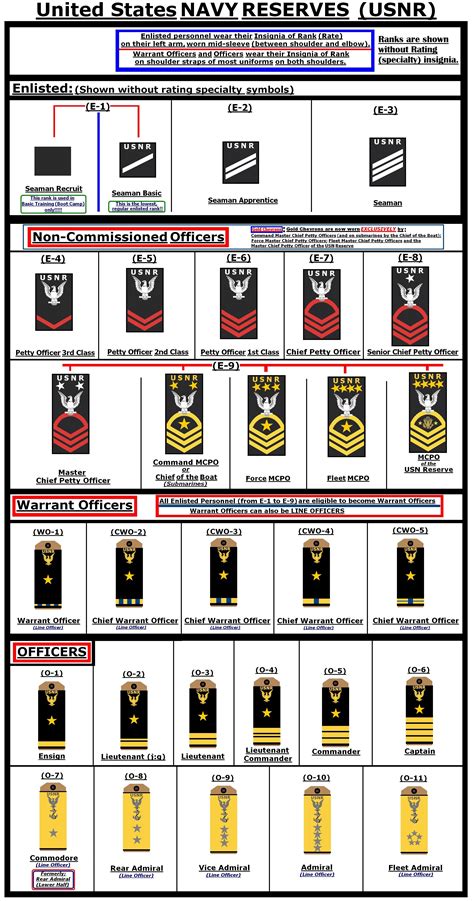
Enlisted Ranks

The enlisted ranks in the navy are the backbone of the force, making up the majority of the personnel. These ranks are divided into several categories, each with its own set of responsibilities: - Seaman Recruit (E-1): The lowest rank in the navy, typically held by new recruits. - Seaman Apprentice (E-2): A junior rank that requires completion of initial training. - Seaman (E-3): A higher rank that requires more experience and training. - Petty Officer Third Class (E-4): The first rank in the non-commissioned officer category, requiring leadership skills and specialized training. - Petty Officer Second Class (E-5): A higher non-commissioned officer rank with more responsibilities. - Petty Officer First Class (E-6): A senior non-commissioned officer rank that requires significant experience and leadership skills. - Chief Petty Officer (E-7): A high-ranking non-commissioned officer with advanced leadership and technical skills. - Senior Chief Petty Officer (E-8): A senior rank that requires extensive experience and expertise. - Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9): The highest enlisted rank in the navy, requiring exceptional leadership and technical skills.
Warrant Officer Ranks
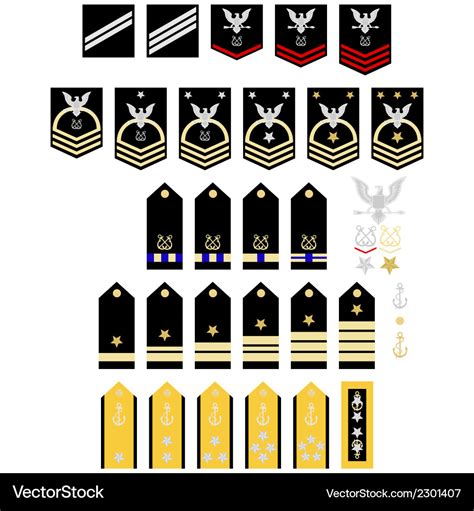
Warrant officers in the navy are technical experts who have risen through the enlisted ranks. They hold a unique position, falling between the enlisted and officer ranks: - Warrant Officer 1 (W-1): The lowest warrant officer rank, requiring specialized technical knowledge. - Chief Warrant Officer 2 (W-2): A higher rank that requires more experience and technical expertise. - Chief Warrant Officer 3 (W-3): A senior warrant officer rank with significant technical and leadership responsibilities. - Chief Warrant Officer 4 (W-4): A high-ranking warrant officer with advanced technical and leadership skills. - Chief Warrant Officer 5 (W-5): The highest warrant officer rank in the navy, requiring exceptional technical expertise and leadership skills.
Commissioned Officer Ranks

Commissioned officers in the navy are responsible for leading and commanding units. They are divided into several categories: - Ensign (O-1): The lowest commissioned officer rank, typically held by new officers. - Lieutenant Junior Grade (O-2): A junior officer rank that requires completion of initial training. - Lieutenant (O-3): A higher officer rank with more responsibilities and leadership duties. - Lieutenant Commander (O-4): A senior officer rank that requires significant experience and leadership skills. - Commander (O-5): A high-ranking officer with advanced leadership and command responsibilities. - Captain (O-6): A senior officer rank with significant command experience and leadership skills. - Rear Admiral (Lower Half) (O-7): The first flag officer rank, requiring exceptional leadership and command skills. - Rear Admiral (Upper Half) (O-8): A higher flag officer rank with more responsibilities and command duties. - Vice Admiral (O-9): A senior flag officer rank with significant command experience and leadership skills. - Admiral (O-10): The highest rank in the navy, requiring exceptional leadership, command, and strategic skills.
| Rank | Pay Grade | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Seaman Recruit | E-1 | Lowest rank in the navy |
| Chief Petty Officer | E-7 | High-ranking non-commissioned officer |
| Commander | O-5 | High-ranking officer with command responsibilities |

📝 Note: The ranks and responsibilities may vary slightly between different countries' naval forces, but the overall structure remains similar.
In summary, the naval hierarchy is a complex system with various ranks and responsibilities. Understanding these ranks is essential for effective communication and cooperation within the naval forces. Whether you’re interested in joining the navy or simply want to learn more about the naval hierarchy, this information provides a comprehensive overview of the different ranks and their roles.
What is the highest rank in the navy?
+The highest rank in the navy is Admiral (O-10), which requires exceptional leadership, command, and strategic skills.
What is the difference between a commissioned officer and a warrant officer?
+A commissioned officer is a leader who has completed a commissioning program, while a warrant officer is a technical expert who has risen through the enlisted ranks.
How do I join the navy?
+To join the navy, you typically need to meet the eligibility requirements, take the ASVAB test, and complete the enlistment process.


