Scores For Asvab Army
Understanding ASVAB Scores for the Army

The Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB) is a multiple-choice test administered by the United States Military Entrance Processing Command. It is used to determine a person’s qualification for enlistment in the military. For those interested in joining the Army, understanding ASVAB scores is crucial as it determines the Military Occupational Specialty (MOS) one can qualify for. The test is divided into nine individual tests, or subtests, which are then combined to form various composite scores, known as line scores.
ASVAB Subtests and Composite Scores
The nine subtests of the ASVAB are: - General Science (GS) - Arithmetic Reasoning (AR) - Word Knowledge (WK) - Paragraph Comprehension (PC) - Mathematics Knowledge (MK) - Electronics Information (EI) - Auto and Shop Information (AS) - Mechanical Comprehension (MC) - Assembling Objects (AO)
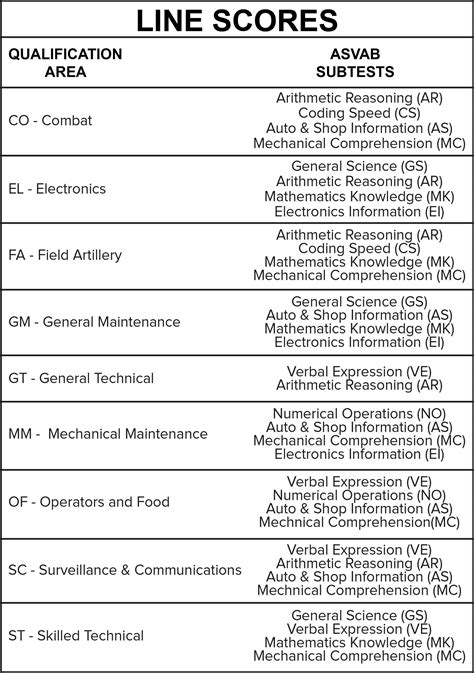
These subtests are then grouped into different combinations to form composite scores or line scores, which are used to determine eligibility for specific Army jobs. The main composite scores for the Army include: - General Technical (GT): Combines AR and WK subtests to determine whether one can be trained for jobs that require a general knowledge of the English language and the ability to solve mathematical problems. - Combat (CO): Combines AS, MC, and AO subtests to assess mechanical aptitude and suitability for combat roles. - Field Artillery (FA): Not a standard line score but can be relevant for certain roles, combining subtests like AR, MK, and MC. - Electronics (EL): Combines GS and EI to determine aptitude for electronics-related jobs. - Mechanical Maintenance (MM): Combines AS, MC, and AO subtests to determine suitability for mechanical maintenance roles. - Surveillance and Communications (SC): Combines WK, PC, and MK subtests.
Interpreting ASVAB Scores

Each subtest is scored from 0 to 100, with the average score set at 50. The highest possible score one can achieve is 99. To be eligible for the Army, one must achieve a minimum score on the Armed Forces Qualification Test (AFQT), which is a combination of AR, WK, PC, and MK subtests. The AFQT score is categorized into five main categories: - Category I: 93-99 (High) - Category II: 65-92 (Above Average) - Category III: 31-64 (Average) - Category IV: 21-30 (Below Average) - Category V: 0-20 (Low)
ASVAB Score Requirements for Army Jobs

Different Army jobs, or Military Occupational Specialties (MOS), require different combinations and levels of ASVAB scores. For example, to qualify for a job like an Infantryman (11X), one might need a Combat (CO) score of 87 or higher, while a job like a Cyber Network Defender (25N) requires a Network Defense (ND) line score of 235 or higher, which is derived from the AR, WK, PC, and MK subtests.
Preparing for the ASVAB
Preparing for the ASVAB involves studying each subtest area. Here are some tips: - Practice Tests: Use practice tests or online resources to assess your current knowledge level. - Study Guides: Utilize study guides or prep books that focus on the ASVAB subtests. - Online Courses: Consider online courses or tutoring for specific areas where you need improvement. - Flashcards: Use flashcards to memorize key terms, especially for the Word Knowledge and General Science sections.
Retaking the ASVAB

If you’re not satisfied with your initial ASVAB scores, you can retake the test after a certain period, usually 30 days, but this can vary depending on the circumstances. It’s essential to prepare well before retaking the test to achieve the desired scores.
💡 Note: Understanding the ASVAB scoring system and preparing well for the test can significantly impact the Military Occupational Specialties one can qualify for, offering a wider range of career options in the Army.
To summarize, ASVAB scores play a critical role in determining one’s eligibility for various roles in the Army. Understanding how these scores are calculated and interpreted, along with preparing well for the test, can significantly impact one’s military career path. Whether one aims for a role in combat, electronics, or another specialty, achieving the required ASVAB scores is the first step towards a successful and fulfilling career in the Army.
What is the minimum AFQT score required to enlist in the Army?
+
The minimum AFQT score required to enlist in the Army is 31, but scores can vary based on the needs of the Army and whether one is enlisting for active duty or the Army Reserve.
How often can I retake the ASVAB?
+
You can retake the ASVAB after 30 days if you’re not satisfied with your initial scores, but there are limits to how many times you can retake the test within a certain timeframe.
What is the difference between the ASVAB and the AFQT?
+
The ASVAB is the overall test that includes nine subtests, while the AFQT (Armed Forces Qualification Test) is a part of the ASVAB that combines four subtests (AR, WK, PC, and MK) to determine overall eligibility for military service.
Can I use my ASVAB scores to qualify for college credits or vocational training?
+
Yes, in some cases, ASVAB scores can be used to qualify for college credits or vocational training, depending on the institution and the scores achieved.