State Salaries Ri
Introduction to State Salaries
The topic of state salaries encompasses a broad range of issues, from the compensation of public employees to the economic impact of government spending on salaries. Understanding state salaries requires an examination of the factors that influence them, the variations across different states, and the implications for public policy. In this discussion, we will delve into the world of state salaries, exploring their complexities and significance.
Factors Influencing State Salaries
Several factors contribute to the determination of state salaries. These include: - Cost of Living: States with a higher cost of living tend to offer higher salaries to compensate for the increased expenses of living in those areas. - Economic Conditions: The economic health of a state, including its budget and revenue, plays a crucial role in determining salary levels. - Job Market and Competition: The demand for certain skills and professions in the private sector can influence public sector salaries, as governments compete for talent. - Union Negotiations and Collective Bargaining: In many cases, public employee unions negotiate salaries and benefits on behalf of their members, which can impact overall salary structures. - Legislative Decisions: Ultimately, state legislatures and governments make decisions about salary scales, often balancing the need to attract and retain quality employees with fiscal responsibilities.
Variations in State Salaries
There is significant variation in state salaries across the United States. Some states offer higher average salaries due to their strong economies, high cost of living, or competitive job markets. For example, states like California and New York tend to have higher salaries, reflecting their high cost of living and the demand for skilled workers. On the other hand, states with lower costs of living and smaller budgets might offer lower salaries. These variations can affect the ability of states to attract and retain skilled public sector employees.
Implications for Public Policy
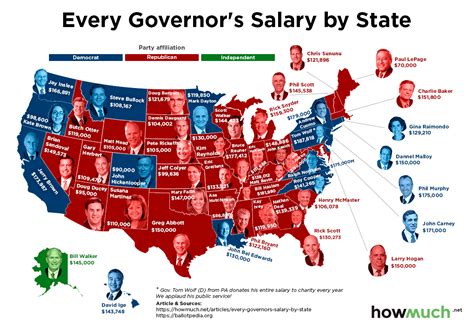
The management and determination of state salaries have significant implications for public policy. Balancing the need to compensate public employees fairly with the fiscal constraints of state budgets is a challenge. Higher salaries can lead to increased government spending, which may require higher taxes or reallocation of funds from other public services. Conversely, low salaries can result in difficulty recruiting and retaining qualified personnel, potentially impacting the quality of public services.
Examples of State Salary Structures
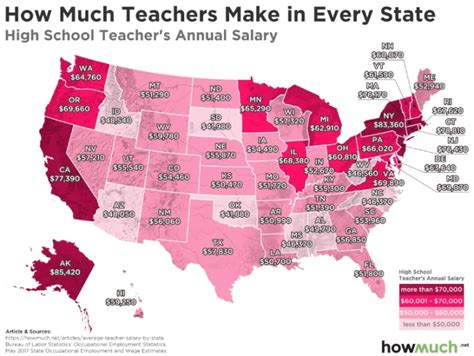
To illustrate the variations in state salaries, let’s consider a few examples: - California: Known for having one of the highest costs of living, California also offers some of the highest state salaries to compensate for this. - Florida: With a lower cost of living compared to California, Florida’s state salaries are generally lower, but the state still competes for talent in areas like education and law enforcement. - Texas: Texas has a strong economy and a relatively low cost of living, which influences its state salary structure, often attracting professionals with competitive salaries without the need for extremely high compensation packages.
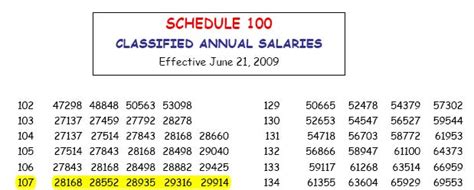
Table of Average State Salaries
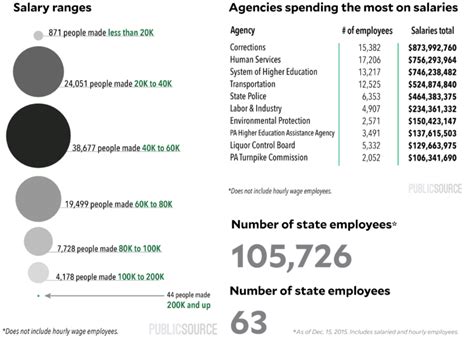
The following table provides a simplified overview of average state salaries for selected professions across a few states:
| State | Average Teacher Salary | Average Police Officer Salary |
|---|---|---|
| California | 82,000</td> <td>73,000 | |
| New York | 76,000</td> <td>69,000 | |
| Florida | 48,000</td> <td>53,000 | |
| Texas | 60,000</td> <td>58,000 |

📝 Note: These figures are examples and may not reflect current or actual average salaries, which can vary widely depending on the source, location within the state, and other factors.
Challenges and Future Directions

Managing state salaries is a complex task that involves addressing current challenges while preparing for future ones. Some of the key challenges include: - Recruitment and Retention: Attracting and keeping skilled employees in a competitive job market. - Fiscal Sustainability: Ensuring that salary structures are sustainable over the long term without overly burdening state finances. - Equity and Fairness: Ensuring that salaries are fair and equitable across different professions and locations within a state.
In conclusion, state salaries are influenced by a multitude of factors and vary significantly across different states. Understanding these variations and the challenges associated with managing state salaries is crucial for developing effective public policies that balance the needs of both public employees and the broader community. The ongoing task for state governments is to navigate these complexities to ensure that they can attract, retain, and fairly compensate the public sector workforce, which is essential for delivering high-quality public services.
What are the primary factors that influence state salaries?
+
The primary factors include the cost of living, economic conditions, job market and competition, union negotiations, and legislative decisions.
How do state salaries vary across the United States?
+
State salaries vary significantly due to differences in the cost of living, economic health, and job market conditions. States like California and New York tend to have higher salaries, while states with lower costs of living may offer lower salaries.
What are the implications of state salaries for public policy?
+
The implications include balancing the need to fairly compensate public employees with the fiscal constraints of state budgets. High salaries can lead to increased government spending, while low salaries can impact the quality of public services due to difficulties in recruiting and retaining qualified personnel.

