Uncover The Ultimate Jrotc Army Ranks

Understanding JROTC Army Ranks: A Comprehensive Guide
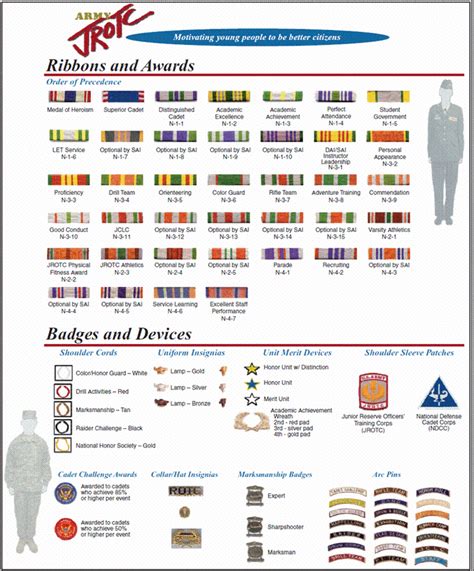
The Junior Reserve Officers’ Training Corps (JROTC) is an important program that introduces high school students to the values and principles of the United States Army. One of the key aspects of JROTC is its rank structure, which mirrors the actual military hierarchy. In this blog post, we will delve into the ultimate JROTC army ranks, exploring their significance, responsibilities, and the path to advancement. Whether you’re a current JROTC cadet or simply curious about the program, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of the JROTC rank system.
Cadet Ranks
JROTC cadets begin their journey at the entry-level rank and work their way up through dedication, hard work, and leadership skills. Let’s explore the cadet ranks in detail:
Private (E-1)
- Rank Description: Private is the starting rank for all JROTC cadets. It is an opportunity for cadets to learn the basics of military discipline, drill, and ceremony.
- Responsibilities: As a Private, cadets focus on mastering the fundamentals, such as military customs and courtesies, proper uniform wear, and basic military knowledge.
Private First Class (E-2)
- Rank Description: Private First Class is the first promotional rank in JROTC. Cadets achieve this rank by demonstrating their understanding of basic military principles and exhibiting good conduct.
- Responsibilities: At this rank, cadets take on more responsibilities, including leading small groups during drills and ceremonies. They also assist in training new cadets.
Corporal (E-4)
- Rank Description: Corporal is a significant step up in the JROTC rank structure. It is often considered the first leadership position.
- Responsibilities: Corporals are responsible for leading squads or teams of cadets. They provide guidance, ensure discipline, and assist in training and mentoring their peers.
Sergeant (E-5)
- Rank Description: Sergeant is a highly respected rank in JROTC, indicating a high level of leadership and responsibility.
- Responsibilities: Sergeants lead larger groups, such as platoons, and are responsible for the overall discipline and performance of their unit. They play a crucial role in planning and executing JROTC activities.
Staff Sergeant (E-6)
- Rank Description: Staff Sergeant is an important rank that bridges the gap between non-commissioned officers and commissioned officers.
- Responsibilities: Staff Sergeants serve as the right-hand men or women to the First Sergeant or Platoon Sergeant. They oversee the daily operations of their unit and ensure that all cadets are meeting the required standards.
Sergeant First Class (E-7)
- Rank Description: Sergeant First Class is a highly prestigious rank, often held by experienced and skilled JROTC cadets.
- Responsibilities: Sergeants First Class are responsible for mentoring and guiding junior non-commissioned officers. They also assist in training and evaluating cadets, ensuring the overall success of the JROTC program.
Master Sergeant (E-8)
- Rank Description: Master Sergeant is the highest non-commissioned officer rank in JROTC. It is a testament to exceptional leadership and dedication.
- Responsibilities: Master Sergeants serve as mentors and advisors to other non-commissioned officers. They play a vital role in maintaining the standards and traditions of the JROTC program.
First Sergeant (E-8)
- Rank Description: First Sergeant is a unique rank, often held by the most senior non-commissioned officer in a JROTC battalion.
- Responsibilities: First Sergeants are responsible for the overall administration and discipline of their battalion. They work closely with the battalion commander and ensure the smooth operation of the program.
Command Sergeant Major (E-9)
- Rank Description: Command Sergeant Major is the highest enlisted rank in JROTC and holds immense prestige.
- Responsibilities: Command Sergeants Major serve as the principal advisor to the JROTC instructor and the battalion commander. They are responsible for the morale, welfare, and professional development of all cadets.
Officer Ranks
In JROTC, officer ranks are typically held by instructors or program administrators. These ranks reflect their leadership and educational roles within the program:
Second Lieutenant (O-1)
- Rank Description: Second Lieutenant is the entry-level officer rank in JROTC. It is often held by recent graduates or experienced cadets who have demonstrated exceptional leadership.
- Responsibilities: Second Lieutenants assist the senior officers in leading and training cadets. They may oversee specific aspects of the program, such as academic instruction or physical training.
First Lieutenant (O-2)
- Rank Description: First Lieutenant is a promotional rank for officers, indicating increased responsibility and experience.
- Responsibilities: First Lieutenants take on more significant leadership roles, often serving as platoon leaders or assistant battalion commanders. They are responsible for the overall performance and development of their assigned units.
Captain (O-3)
- Rank Description: Captain is a highly respected rank in JROTC, often held by experienced officers.
- Responsibilities: Captains serve as battalion commanders or senior administrators. They are responsible for the overall management and success of the JROTC program, including curriculum development and cadet recruitment.
Major (O-4)
- Rank Description: Major is a senior officer rank, indicating a high level of expertise and leadership.
- Responsibilities: Majors often serve as executive officers or program coordinators. They assist the battalion commander in making strategic decisions and ensuring the smooth operation of the program.
Lieutenant Colonel (O-5)
- Rank Description: Lieutenant Colonel is a prestigious rank, held by experienced and respected officers.
- Responsibilities: Lieutenant Colonels typically serve as the JROTC instructor or program director. They are responsible for the overall administration, instruction, and supervision of the JROTC program.
Colonel (O-6)
- Rank Description: Colonel is the highest officer rank in JROTC, held by the most senior and experienced instructors.
- Rank Description: Colonels are responsible for the long-term strategic planning and development of the JROTC program. They ensure that the program aligns with the goals and objectives of the Army and the school district.
Path to Advancement
Advancing through the JROTC ranks requires a combination of dedication, leadership skills, and academic achievement. Here are some key factors that contribute to rank advancement:
- Leadership: Demonstrating strong leadership qualities and taking initiative are crucial for rank advancement. Cadets who lead by example and inspire their peers are often recognized for their efforts.
- Academic Performance: Maintaining good grades and academic excellence is essential. JROTC places a strong emphasis on education, and cadets who excel academically are more likely to be considered for promotions.
- Participation and Attendance: Regular attendance and active participation in JROTC activities are vital. Cadets who consistently attend drills, ceremonies, and extracurricular events are more likely to be noticed for their dedication.
- Performance Evaluations: JROTC instructors conduct periodic performance evaluations to assess cadets’ progress and leadership skills. Positive evaluations can significantly impact rank advancement.
- Extra-curricular Activities: Engaging in extra-curricular activities, such as community service or sports, can demonstrate a cadet’s well-rounded character and commitment to personal growth.
Conclusion
The JROTC army rank structure is a crucial aspect of the program, fostering leadership, discipline, and a sense of responsibility among high school students. By understanding the ranks and their respective responsibilities, cadets can work towards their goals and contribute to the success of the JROTC program. Whether you’re a cadet aspiring to reach the highest ranks or simply exploring the world of JROTC, this guide has provided you with valuable insights into the ultimate JROTC army ranks. Remember, JROTC is not just about military training; it’s about developing well-rounded individuals who can make a positive impact on their communities.
FAQ

Can I join JROTC if I have no prior military experience?
+Absolutely! JROTC is open to all high school students, regardless of their military background. It is an excellent opportunity to learn about the military and develop leadership skills.
What are the benefits of participating in JROTC?
+JROTC offers numerous benefits, including leadership development, improved discipline, enhanced physical fitness, and the opportunity to earn college scholarships. It also provides a strong foundation for those considering a military career.
Can I advance to higher ranks without being a top performer academically or in leadership?
+While academic and leadership excellence are important factors, JROTC also considers other aspects such as attendance, participation, and improvement. Showing dedication and a willingness to learn can still lead to rank advancement.
Are there any age restrictions for joining JROTC?
+JROTC is typically offered to high school students, so the age range varies depending on the school’s policy. However, most programs accept students from 14 to 18 years old.
Can I join JROTC if I have a physical disability?
+JROTC programs aim to be inclusive and accommodate students with physical disabilities. While some physical activities may be modified, JROTC still offers valuable leadership and educational opportunities.