United States Navy Reserve Fleets

Introduction to the United States Navy Reserve Fleets

The United States Navy Reserve is a vital component of the country’s naval power, providing a pool of trained personnel who can be called upon to support the active-duty Navy in times of war or national emergency. The Navy Reserve has a long history, dating back to 1915, and has played a significant role in several major conflicts, including World War I, World War II, the Korean War, and the Vietnam War. One of the key elements of the Navy Reserve is its fleet structure, which is designed to provide a flexible and responsive force that can be tailored to meet the needs of the active-duty Navy.
Organization of the Navy Reserve Fleets

The Navy Reserve is organized into several fleets, each of which is responsible for a specific geographic area or functional specialty. The fleets are typically commanded by a rear admiral, who is responsible for the overall administration and operation of the fleet. The fleets are further divided into smaller units, such as squadrons, groups, and detachments, which are commanded by officers of lower rank. The Navy Reserve fleets are organized into the following components: * Navy Reserve Fleet Forces Command: This command is responsible for the overall administration and operation of the Navy Reserve fleets. * Navy Reserve Pacific Fleet: This fleet is responsible for the Pacific Ocean area and is headquartered in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. * Navy Reserve Atlantic Fleet: This fleet is responsible for the Atlantic Ocean area and is headquartered in Norfolk, Virginia. * Navy Reserve Naval Air Force: This command is responsible for the Navy Reserve’s aviation assets, including aircraft squadrons and air stations.
Types of Navy Reserve Fleets

The Navy Reserve has several types of fleets, each with its own unique mission and responsibilities. Some of the main types of Navy Reserve fleets include: * Cruiser-Destroyer Fleet: This fleet is composed of cruisers and destroyers, which are designed to provide surface warfare capabilities. * Aircraft Carrier Fleet: This fleet is composed of aircraft carriers, which are designed to provide air power capabilities. * Amphibious Fleet: This fleet is composed of amphibious ships, which are designed to provide landing craft and other assets for amphibious assaults. * Submarine Fleet: This fleet is composed of submarines, which are designed to provide underwater warfare capabilities. * Logistics Fleet: This fleet is composed of supply ships and other logistics assets, which are designed to provide support to the other fleets.
Functions of the Navy Reserve Fleets
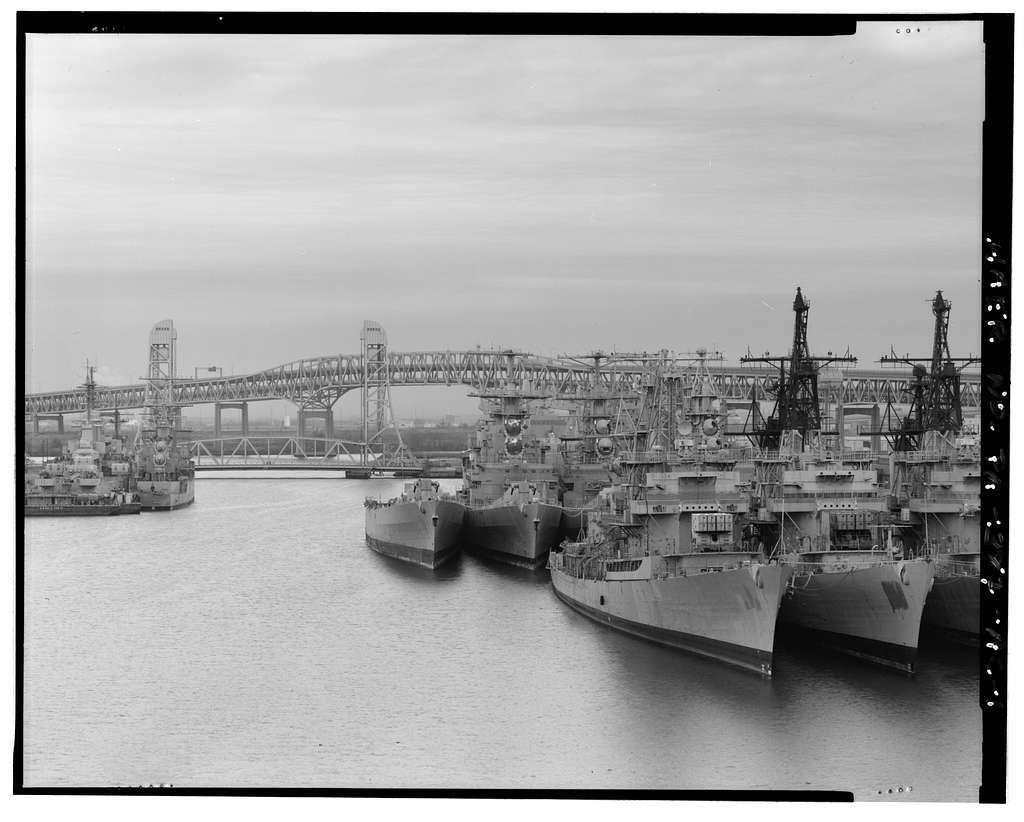

The Navy Reserve fleets have several key functions, including: * Training and Exercises: The Navy Reserve fleets participate in regular training exercises to maintain their readiness and proficiency. * Support to Active-Duty Navy: The Navy Reserve fleets provide support to the active-duty Navy, including personnel, equipment, and logistics. * Humanitarian Assistance: The Navy Reserve fleets participate in humanitarian assistance missions, such as disaster relief and humanitarian aid. * Homeland Defense: The Navy Reserve fleets participate in homeland defense missions, such as port security and maritime patrol.
Benefits of the Navy Reserve Fleets

The Navy Reserve fleets provide several benefits, including: * Cost Savings: The Navy Reserve fleets are a cost-effective way to maintain a large and capable naval force. * Increased Readiness: The Navy Reserve fleets provide a pool of trained personnel who can be called upon to support the active-duty Navy in times of war or national emergency. * Improved Flexibility: The Navy Reserve fleets provide a flexible and responsive force that can be tailored to meet the needs of the active-duty Navy. * Enhanced Capabilities: The Navy Reserve fleets provide a range of capabilities, including surface warfare, air power, amphibious assault, and underwater warfare.
| Fleet | Location | Commander |
|---|---|---|
| Navy Reserve Fleet Forces Command | Norfolk, Virginia | Rear Admiral |
| Navy Reserve Pacific Fleet | Rear Admiral | |
| Navy Reserve Atlantic Fleet | Norfolk, Virginia | Rear Admiral |

📝 Note: The information provided in this table is subject to change and may not reflect the current organization or leadership of the Navy Reserve fleets.
In summary, the United States Navy Reserve fleets play a vital role in supporting the active-duty Navy and providing a range of capabilities to meet the needs of the nation. The fleets are organized into several components, including the Navy Reserve Fleet Forces Command, Navy Reserve Pacific Fleet, and Navy Reserve Atlantic Fleet, and are responsible for a range of functions, including training and exercises, support to active-duty Navy, humanitarian assistance, and homeland defense. The Navy Reserve fleets provide several benefits, including cost savings, increased readiness, improved flexibility, and enhanced capabilities.
What is the primary function of the Navy Reserve fleets?
+
The primary function of the Navy Reserve fleets is to provide a pool of trained personnel who can be called upon to support the active-duty Navy in times of war or national emergency.
What are the main types of Navy Reserve fleets?
+
The main types of Navy Reserve fleets include the Cruiser-Destroyer Fleet, Aircraft Carrier Fleet, Amphibious Fleet, Submarine Fleet, and Logistics Fleet.
What are the benefits of the Navy Reserve fleets?
+
The benefits of the Navy Reserve fleets include cost savings, increased readiness, improved flexibility, and enhanced capabilities.