Us Coast Guard Officer Ranks
Introduction to US Coast Guard Officer Ranks

The United States Coast Guard is a unique branch of the US military, operating under the Department of Homeland Security during peacetime and under the Department of the Navy during wartime. The Coast Guard’s mission is to protect the public, the environment, and the United States’ economic and security interests in any maritime region, including international waters and America’s coasts, ports, and inland waterways. The officer ranks within the US Coast Guard are structured to reflect the organization’s dual role as both a military service and a law enforcement agency. Understanding these ranks is essential for anyone interested in a career with the Coast Guard or for those who want to learn more about the structure of this vital service.
Officer Ranks in the US Coast Guard
The officer ranks in the US Coast Guard are divided into several categories, starting from the most junior to the most senior: Ensign (ENS), Lieutenant Junior Grade (LTJG), Lieutenant (LT), Lieutenant Commander (LCDR), Commander (CDR), Captain (CAPT), Rear Admiral (Lower Half) (RDML), Rear Admiral (Upper Half) (RADM), Vice Admiral (VA), and Admiral (ADM). Each rank has its own set of responsibilities and requirements for advancement.
- Ensign (ENS): The most junior officer rank, typically held by new officers upon commissioning.
- Lieutenant Junior Grade (LTJG): A junior officer rank, often serving in a division officer role.
- Lieutenant (LT): Serves as a department head or executive officer on smaller cutters.
- Lieutenant Commander (LCDR): Often serves as executive officer on larger cutters or as department head on major cutters.
- Commander (CDR): May command smaller cutters or serve as executive officer on larger ships.
- Captain (CAPT): Commands larger cutters or serves in senior staff positions ashore.
- Rear Admiral (Lower Half) (RDML) and Rear Admiral (Upper Half) (RADM): One-star and two-star admirals, respectively, who serve in various senior leadership positions.
- Vice Admiral (VA): A three-star admiral, often serving as the Vice Commandant of the Coast Guard.
- Admiral (ADM): The highest rank, typically held by the Commandant of the Coast Guard.
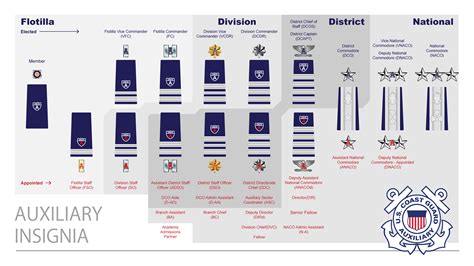
Rank Insignia and Uniforms

The rank insignia for Coast Guard officers are worn on the sleeves of their service dress blue uniforms and on the collars of their service dress whites and tropical blues. The insignia consist of stripes (for junior officers) and stars (for senior officers). The specific design and placement of these insignia can distinguish between ranks and provide a visible indication of an officer’s status within the Coast Guard.
Education and Training

To become an officer in the US Coast Guard, one must meet specific educational and training requirements. These can include graduating from the United States Coast Guard Academy, completing Officer Candidate School (OCS), or receiving a commission through a direct commission program. Once commissioned, officers undergo initial training specific to their designator (job specialty) and continue their professional development throughout their careers, attending various courses and receiving on-the-job training.
Role of Officers in the US Coast Guard

Officers in the US Coast Guard play a critical role in leading the service’s diverse missions, from maritime law enforcement and search and rescue to marine safety and environmental protection. They are responsible for making strategic decisions, overseeing operations, and ensuring the readiness and morale of their units. Whether serving afloat or ashore, Coast Guard officers are expected to embody the service’s core values of honor, respect, and devotion to duty.
💡 Note: The path to becoming a Coast Guard officer is highly competitive, and meeting the basic requirements does not guarantee acceptance into the officer training programs.
Comparison with Other Military Branches

The rank structure of the US Coast Guard is similar to that of the US Navy, reflecting their shared maritime mission and historical ties. However, the Coast Guard’s unique role as a law enforcement agency and its responsibility for a wide range of civilian missions set it apart from the other military branches. Understanding these differences is crucial for anyone considering a career in the Coast Guard, as the service’s distinct culture and operational focus can significantly impact an officer’s experience and opportunities.
| Rank | US Coast Guard | US Navy |
|---|---|---|
| Junior Officer | Ensign (ENS) | Ensign (ENS) |
| Senior Officer | Captain (CAPT) | Captain (CAPT) |
| Flag Officer | Rear Admiral (RADM) | Rear Admiral (RADM) |

As the US Coast Guard continues to evolve and face new challenges, its officer corps remains at the forefront, leading the service in its multifaceted mission to protect the United States and its interests. The leadership and expertise provided by Coast Guard officers are indispensable to the success of the service, ensuring that the Coast Guard remains “Semper Paratus” - always ready.
In summary, the officer ranks in the US Coast Guard are designed to meet the service’s unique blend of military and law enforcement responsibilities. From the junior officer ranks to the flag officers, each level of leadership plays a critical role in the Coast Guard’s operations and readiness. Understanding these ranks and the responsibilities they entail is essential for appreciating the complexity and importance of the Coast Guard’s mission.
What are the requirements to become a US Coast Guard officer?
+To become a US Coast Guard officer, one must meet specific educational and physical requirements, and then attend the Coast Guard Academy, Officer Candidate School, or receive a direct commission.
How do US Coast Guard ranks compare to US Navy ranks?
+The rank structures of the US Coast Guard and US Navy are very similar, reflecting their shared maritime missions. However, the Coast Guard has a unique set of responsibilities and a distinct culture.
What is the highest rank in the US Coast Guard?
+The highest rank in the US Coast Guard is Admiral (ADM), typically held by the Commandant of the Coast Guard.