Us Fault Lines Map
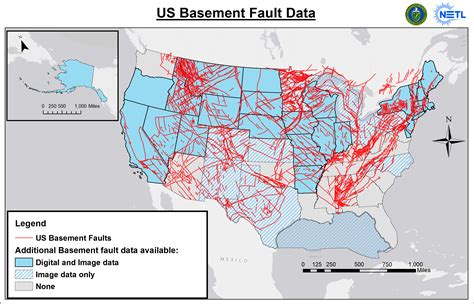
Understanding the complex network of fault lines across the United States is crucial for both scientific research and public safety. This comprehensive guide aims to provide an in-depth exploration of the major fault lines in the US, their historical significance, and their potential impact on the nation's geological future.
The San Andreas Fault: A Focal Point of Geological Study

Undoubtedly, the San Andreas Fault is one of the most renowned and extensively studied fault lines in the world. Stretching across California, this fault has been responsible for some of the most significant earthquakes in US history, including the famous 1906 San Francisco earthquake.
The San Andreas Fault is a transform fault, meaning it forms the boundary between two tectonic plates, in this case, the North American Plate and the Pacific Plate. As these plates slide past each other, the resulting friction and pressure can lead to seismic activity. Over time, this fault has shaped the unique geological landscape of California, creating iconic features like the Salton Sea and the San Andreas Rift Zone.
Other Notable Fault Lines in the Western US

While the San Andreas Fault takes center stage, several other fault lines in the Western US deserve attention.
The Hayward Fault
Running through the East Bay region of the San Francisco Bay Area, the Hayward Fault is considered one of the most dangerous in the US due to its proximity to densely populated areas. This fault has the potential to produce a major earthquake, with the last significant event occurring in 1868.
The New Madrid Seismic Zone
Located in the central US, the New Madrid Seismic Zone is responsible for some of the largest earthquakes ever recorded in North America. In 1811 and 1812, a series of powerful earthquakes struck this region, causing widespread damage and even temporarily reversing the flow of the Mississippi River.
The Wasatch Fault
Spanning parts of Utah, Idaho, and Wyoming, the Wasatch Fault is a major source of concern for geologists and residents alike. This fault has the potential to generate earthquakes of magnitude 7.5 or higher, which could have devastating consequences for the Salt Lake City metropolitan area.
Eastern US Fault Lines: Unveiling Hidden Geological Hazards

While most people associate fault lines with the Western US, the Eastern part of the country also has its fair share of geological faults. These faults, though less active, can still pose significant risks.
The Ramapo Fault
Stretching from New Jersey into New York, the Ramapo Fault is a major boundary between the North American Plate and the Atlantic Plate. While not as active as some of its Western counterparts, the Ramapo Fault has the potential to generate earthquakes, with the last significant event occurring in 1884.
The Central Virginia Seismic Zone
In 2011, the Eastern US was reminded of its seismic potential with the Virginia earthquake. This event, though relatively minor, highlighted the existence of the Central Virginia Seismic Zone, which has the potential to produce earthquakes of moderate intensity.
Understanding Fault Lines: A Key to Earthquake Prediction
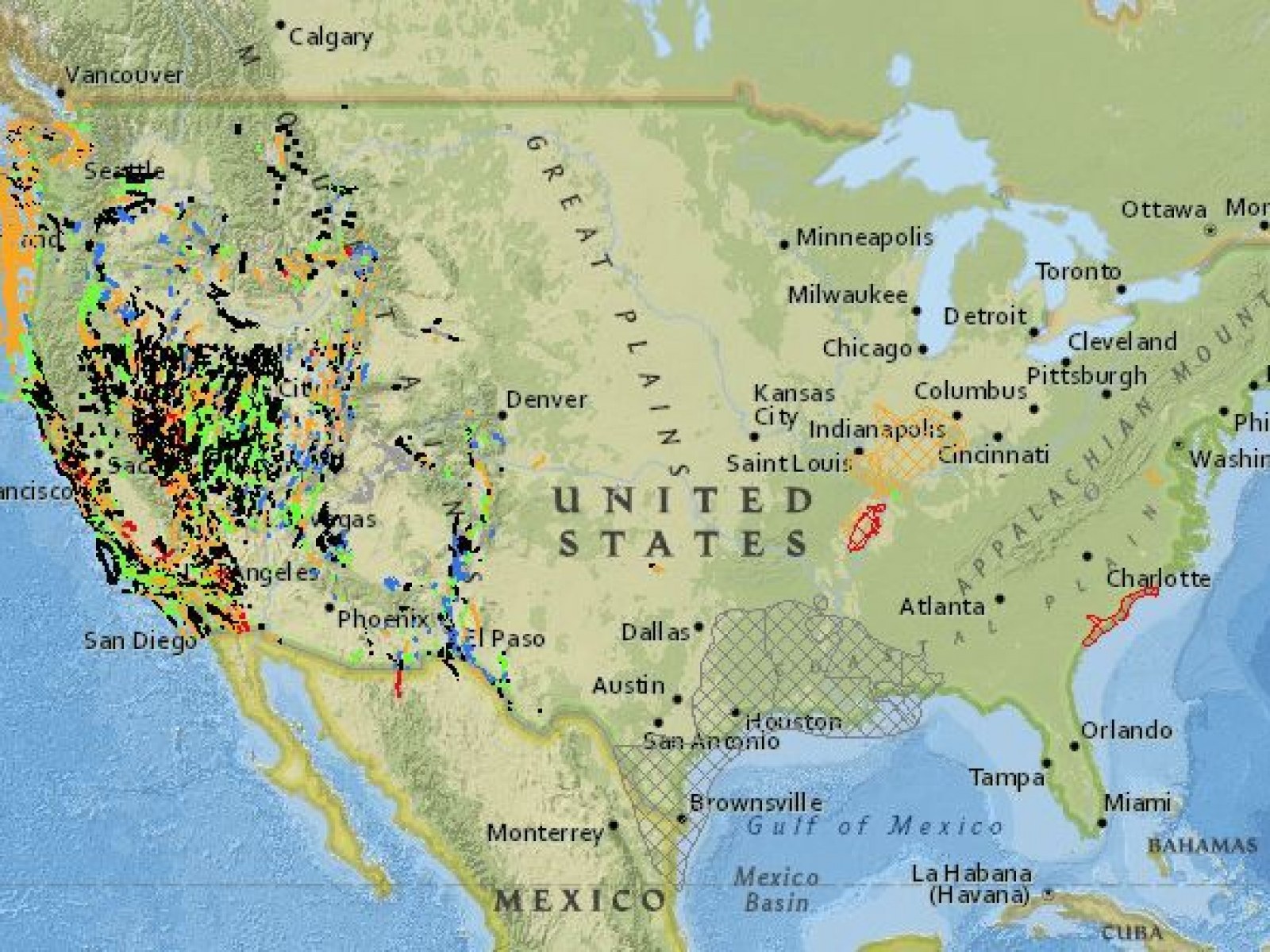
Studying fault lines is not just about understanding past earthquakes; it’s also about predicting future seismic events. By analyzing the movement and behavior of these faults, geologists can develop models to forecast potential earthquake activity.
One of the key tools in this endeavor is the use of GPS technology. By monitoring the subtle movements of the Earth's surface, scientists can detect the buildup of strain along fault lines, providing valuable insights into the likelihood of an earthquake.
The Role of Technology in Fault Line Monitoring
Advancements in technology have revolutionized the way fault lines are studied and monitored. Besides GPS, other technologies such as seismic sensors, satellite imagery, and even drone technology are being employed to gather data and create detailed maps of fault zones.
These technologies not only help in the immediate detection of earthquakes but also provide long-term data for research and planning. By continuously monitoring fault lines, scientists can identify patterns and make more accurate predictions about future seismic activity.
The Impact of Fault Lines on Urban Planning

The presence of fault lines has significant implications for urban planning and development. Cities and towns located near active faults must consider the potential risks when designing infrastructure and emergency response plans.
For instance, building codes in areas with high seismic activity often require structures to be designed with earthquake-resistant features. This includes the use of specific construction materials, reinforcement techniques, and even innovative designs to minimize the impact of earthquakes.
Community Education and Preparedness

While scientists and urban planners play a crucial role in mitigating the risks associated with fault lines, community education and preparedness are equally important. Residents living in earthquake-prone areas should be aware of the potential risks and know how to respond in the event of an earthquake.
This includes understanding the basic principles of earthquake safety, such as identifying safe places in a home or building, knowing how to shut off utilities, and having an emergency kit ready. Regular drills and community education programs can help ensure that residents are well-prepared for any potential seismic event.
Conclusion

The study of fault lines in the US is a multifaceted endeavor, encompassing geology, seismology, urban planning, and community preparedness. By understanding the complex network of fault lines across the nation, we can better prepare for and mitigate the impact of earthquakes, ensuring the safety and resilience of our communities.
What is the most active fault line in the US?
+The San Andreas Fault in California is considered the most active and well-known fault line in the US, responsible for some of the most significant earthquakes in the nation’s history.
Are there fault lines in the Eastern US?
+Yes, the Eastern US has several fault lines, including the Ramapo Fault and the Central Virginia Seismic Zone. While less active than their Western counterparts, these faults can still pose risks to the region.
How do scientists monitor fault lines for potential earthquakes?
+Scientists use a variety of technologies, including GPS, seismic sensors, and satellite imagery, to monitor fault lines for signs of strain and potential earthquake activity. This data is crucial for developing earthquake prediction models.
What can individuals do to prepare for earthquakes in fault line areas?
+Individuals living in fault line areas should educate themselves about earthquake safety, create emergency plans and kits, and participate in community preparedness programs to ensure they are ready for any potential seismic event.
