Us Military Organization Chart

Introduction to the US Military Organization Chart
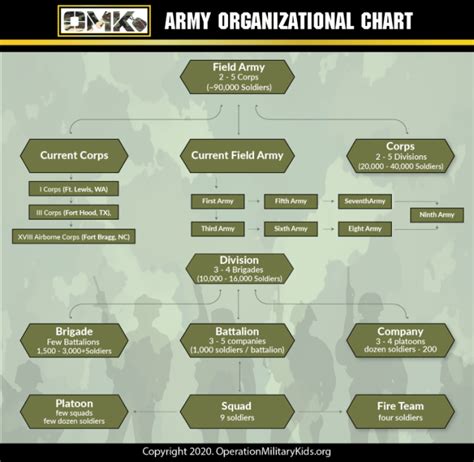
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States of America. It consists of five branches: the United States Army, United States Navy, United States Air Force, United States Marine Corps, and the United States Coast Guard. The US military is one of the largest and most technologically advanced military forces in the world. Understanding the organization of the US military can be complex due to its size and the various units within each branch. This article aims to provide an overview of the structure of the US military and how its different components work together.
Chain of Command
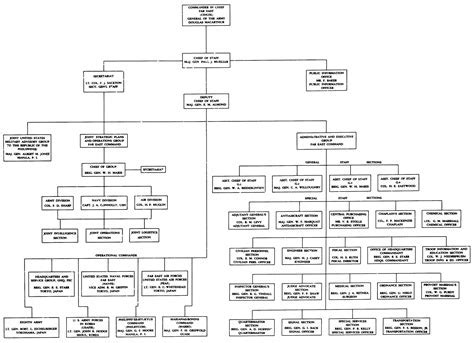
At the top of the US military organization chart is the President of the United States, who serves as the Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces. The President is responsible for making key decisions regarding national security and defense. Below the President is the Secretary of Defense, who is the head of the Department of Defense (DoD). The Secretary of Defense is responsible for the formulation and implementation of policies related to national security and defense.
Department of Defense (DoD)

The Department of Defense is divided into several branches, each with its own unique responsibilities and structures. The main branches include: - United States Army: responsible for land-based military operations. - United States Navy: responsible for naval operations. - United States Air Force: responsible for air-based military operations. - United States Marine Corps: a rapid-response force that specializes in ground combat. - United States Coast Guard: responsible for maritime law enforcement, search and rescue, and marine safety.
Operational Structure
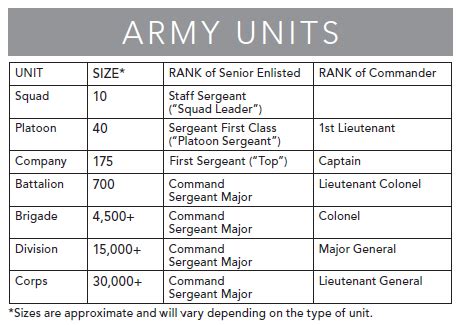
Each branch of the US military has its own operational structure: - Army: divided into divisions, which are further divided into brigades, battalions, companies, platoons, and squads. - Navy: organized into fleets, which consist of ships and submarines, and are supported by naval aviation and marine units. - Air Force: composed of wings, which are made up of groups, squadrons, and flights. - Marine Corps: structured into divisions, which are divided into regiments, battalions, companies, platoons, and squads. - Coast Guard: organized into districts, which are further divided into sectors and units.
Unified Combatant Commands

The US military also operates under a system of Unified Combatant Commands (UCCs), which are joint military commands that combine forces from two or more military branches to achieve strategic objectives. There are currently eleven UCCs, each with a specific geographic or functional responsibility: - Africa Command (AFRICOM) - Central Command (CENTCOM) - European Command (EUCOM) - Indo-Pacific Command (INDOPACOM) - Northern Command (NORTHCOM) - Southern Command (SOUTHCOM) - Space Command (SPACECOM) - Special Operations Command (SOCOM) - Strategic Command (STRATCOM) - Transportation Command (TRANSCOM)
Military Ranks

Understanding military ranks is crucial for grasping the hierarchy within the US military. Ranks vary slightly between branches but generally follow a similar structure: - Enlisted Ranks: range from Private (E-1) to Sergeant Major (E-9) in the Army and Marine Corps, and from Seaman Recruit (E-1) to Master Chief Petty Officer (E-9) in the Navy and Coast Guard. - Warrant Officer Ranks: technical specialists who are considered experts in their field, ranging from W-1 to W-5. - Officer Ranks: from Second Lieutenant (O-1) to General (O-10) in the Army, Air Force, and Marine Corps, and from Ensign (O-1) to Admiral (O-10) in the Navy and Coast Guard.
Key Roles and Responsibilities
Each member of the US military, regardless of rank or branch, plays a vital role in the overall effectiveness of the Armed Forces. Key roles include: - Combat Roles: directly involved in combat operations. - Support Roles: provide essential services such as logistics, medical care, and communications. - Administrative Roles: manage the day-to-day operations of military units.
Challenges and Future Directions
The US military faces numerous challenges, including technological advancements, cybersecurity threats, and global instability. To address these challenges, the military is investing in modernization efforts, enhancing its cyber capabilities, and fostering international partnerships to promote global security and stability.
📝 Note: The structure and organization of the US military can change over time due to reforms and reorganizations, making it essential to stay updated on the latest developments.
In summary, the US military organization chart is complex, with a hierarchical structure that spans from the President as the Commander-in-Chief down to the enlisted personnel. Understanding this structure is crucial for appreciating the functioning and effectiveness of the US Armed Forces. The military’s ability to adapt to new challenges and technologies will be key to its success in the future. As the global security landscape continues to evolve, the importance of a strong, well-organized military cannot be overstated.
What are the main branches of the US military?
+The main branches of the US military include the United States Army, United States Navy, United States Air Force, United States Marine Corps, and the United States Coast Guard.
Who is at the top of the US military organization chart?
+The President of the United States serves as the Commander-in-Chief of the Armed Forces, making key decisions regarding national security and defense.
What is the role of the Department of Defense (DoD)?
+The Department of Defense is responsible for the formulation and implementation of policies related to national security and defense, overseeing the entire US military organization.



