What Infantry Does: A Comprehensive Guide To Their Essential Role

The infantry forms the backbone of any military force, playing a crucial and multifaceted role on the battlefield. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various aspects of what infantry does, shedding light on their essential functions and contributions to military operations.
The Core Responsibilities of Infantry
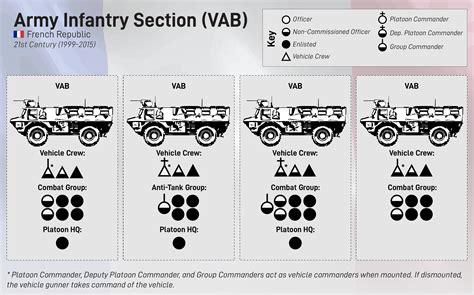
Infantry soldiers are highly trained individuals who specialize in ground combat. Their primary role is to engage in close-quarters combat, utilizing their skills and weaponry to gain and maintain control over designated areas. Here are some key responsibilities that define the infantry's role:
- Assault and Capture: Infantry units are tasked with conducting assaults on enemy positions, whether it's a fortified stronghold or a strategic location. Their training and tactics enable them to breach defenses and secure objectives.
- Defense and Protection: Infantry soldiers are often the first line of defense, responsible for protecting their fellow soldiers and vital assets. They establish defensive positions, set up perimeters, and engage in counter-attacks to repel enemy advances.
- Reconnaissance and Intelligence Gathering: Infantry teams are deployed for reconnaissance missions, gathering vital intelligence about enemy movements, positions, and activities. This information is crucial for planning and executing successful military operations.
- Urban Warfare: Infantry soldiers are experts in urban combat, navigating through cities and towns to engage enemy forces in built-up areas. Their training equips them with the skills to adapt to complex urban environments and clear buildings effectively.
- Patrolling and Surveillance: Infantry units conduct patrols to maintain a constant presence in designated areas. They monitor enemy activity, deter potential threats, and provide early warning of any hostile actions.
- Specialized Tasks: Infantry soldiers may also be trained for specific tasks such as sniper operations, counter-insurgency, or conducting raids. Their versatility allows them to adapt to various combat scenarios.
The Infantry's Role in Modern Warfare

In the ever-evolving landscape of modern warfare, the infantry's role has adapted to meet new challenges. Here's how infantry units contribute to contemporary military operations:
- Light Infantry: These infantry units are designed for rapid deployment and mobility. They are often air-transported to remote areas, allowing for swift reaction to emerging threats.
- Mechanized Infantry: Equipped with armored vehicles, mechanized infantry provides enhanced mobility and protection. They can quickly respond to changing situations and offer support to other units.
- Mountain Infantry: Specialized in operating in mountainous terrain, these infantry units are trained to navigate and fight in challenging environments. Their expertise is invaluable in regions with rugged topography.
- Paratroopers: Paratroopers are infantry soldiers trained for airborne operations. They are deployed via parachute, allowing for strategic insertion into enemy-controlled areas.
- Special Forces: Highly trained and specialized infantry units, such as the Special Air Service (SAS) or the Navy SEALs, undertake high-risk missions that demand precision and stealth.
Training and Equipment

The effectiveness of infantry units is heavily reliant on their training and equipment. Infantry soldiers undergo rigorous training programs that cover a wide range of skills, including:
- Firearms Proficiency: Infantry soldiers are trained to handle various firearms, from assault rifles to machine guns and specialized weapons.
- Tactical Movement: They learn how to move efficiently in combat situations, utilizing cover and concealment to their advantage.
- Fieldcraft: Infantry soldiers master the art of survival and navigation in diverse environments, from deserts to forests.
- Urban Warfare Techniques: Specialized training in urban combat teaches them how to clear buildings, engage in close-quarters combat, and navigate through urban landscapes.
- Teamwork and Communication: Infantry units operate as cohesive teams, and effective communication is vital for their success.
In terms of equipment, infantry soldiers are equipped with a range of weapons and gear tailored to their specific role. This includes assault rifles, machine guns, grenades, body armor, communication devices, and specialized equipment for specific missions.
The Infantry's Impact on Military Strategy
The infantry's role extends beyond the battlefield. Their presence and actions can have a significant impact on military strategy and the overall outcome of a conflict. Here's how:
- Influence on Tactical Decisions: Infantry units provide crucial ground control, which influences the decisions made by military commanders. Their ability to secure and hold territory can shape the direction of an entire campaign.
- Intelligence and Reconnaissance: The intelligence gathered by infantry reconnaissance teams is invaluable for military planners. It helps identify enemy weaknesses, plan attacks, and make informed strategic decisions.
- Morale and Motivation: Infantry soldiers often serve as the backbone of a military force, boosting morale and motivating their fellow soldiers. Their bravery and dedication can inspire others to persevere in the face of adversity.
The Challenges of Infantry Operations

While the infantry plays a vital role, they also face unique challenges on the battlefield. Some of the key challenges include:
- Urban Combat: Operating in urban environments presents a range of challenges, from navigating through complex buildings to dealing with enemy forces hiding among civilians.
- Close-Quarters Combat: Infantry soldiers often engage in intense close-quarters combat, where every decision and action can have life-or-death consequences.
- Logistical Support: Infantry units require a constant supply of ammunition, food, and other essential resources. Ensuring timely and efficient logistical support is crucial for their success.
- Casualty Management: Infantry operations can result in casualties, and managing these casualties effectively is a significant challenge. Quick and efficient medical support is essential to save lives.
The Evolution of Infantry Tactics

Throughout history, infantry tactics have evolved to meet the changing nature of warfare. Here are some key developments:
- Line Infantry: In the early days of warfare, infantry soldiers fought in tightly packed lines, firing in unison. This formation provided a powerful volley of fire but was vulnerable to flanking maneuvers.
- Column Formation: The column formation allowed infantry units to move quickly and in a more compact manner, making it suitable for rapid deployment and flanking maneuvers.
- Skirmish Lines: Skirmish lines were adopted to provide a more flexible and dispersed formation, allowing infantry soldiers to engage the enemy from multiple angles.
- Fire and Movement: Modern infantry tactics emphasize the concept of fire and movement, where soldiers provide covering fire while others advance or maneuver.
- Combined Arms: The integration of infantry with other military branches, such as armor and artillery, has become a key tactic, allowing for more effective and coordinated attacks.
The Future of Infantry

As technology continues to advance, the future of infantry operations is likely to see further innovations. Here are some potential developments:
- Enhanced Mobility: Infantry units may be equipped with advanced exoskeletons or powered armor, increasing their mobility and protection.
- Improved Communication: Advances in communication technology will enable better coordination and real-time intelligence sharing among infantry teams.
- Unmanned Systems: Infantry units may utilize unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and robotic systems for reconnaissance, surveillance, and even combat support.
- Biometric Identification: Biometric technology could be employed to identify enemy combatants, reducing the risk of civilian casualties.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI-powered systems may assist infantry soldiers in making tactical decisions and analyzing battlefield data.
The infantry remains an indispensable component of any military force, and their role continues to evolve to meet the challenges of modern warfare. Their bravery, dedication, and skill make them a force to be reckoned with on the battlefield.
What is the average infantry soldier’s age and physical condition?
+The average age of an infantry soldier can vary depending on the military branch and country. In general, infantry soldiers are typically in their early 20s to mid-30s, with a focus on physical fitness and combat readiness.
How long does it take to train an infantry soldier?
+The training duration for infantry soldiers varies. Basic training typically lasts several months, followed by advanced infantry training that can range from a few weeks to several months. Additional specialized training may also be required for certain roles.
What are some common weapons used by infantry soldiers?
+Infantry soldiers are equipped with a range of weapons, including assault rifles (such as the M4 or AK-47), machine guns (like the M249 or PKM), grenades, and specialized weapons like sniper rifles or anti-tank weapons.
Do infantry soldiers work alone, or are they part of a larger team?
+Infantry soldiers typically operate as part of a team or squad, with each member having a specific role and responsibility. Working together as a cohesive unit is crucial for their effectiveness and survival on the battlefield.
What are some notable historical infantry battles or campaigns?
+Throughout history, there have been numerous notable infantry battles and campaigns. Some examples include the Battle of Bunker Hill during the American Revolution, the Battle of Stalingrad in World War II, and the Battle of Mogadishu in Somalia.


