What Is Frequency Measured In
Frequency is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering, and it plays a crucial role in various fields, including acoustics, electronics, and telecommunications. It is a measure of how often a particular event or cycle occurs within a specific time frame. Understanding frequency is essential for analyzing and manipulating signals, waves, and oscillations. In this blog post, we will explore what frequency is, how it is measured, and its significance in different applications.
Understanding Frequency

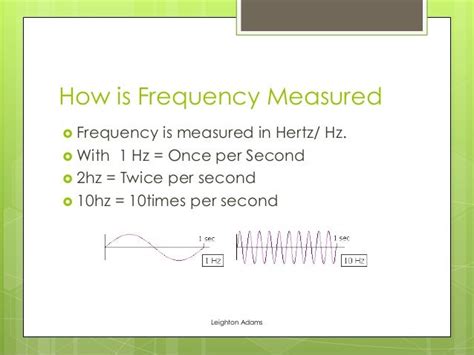
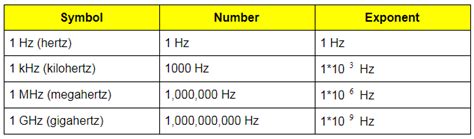
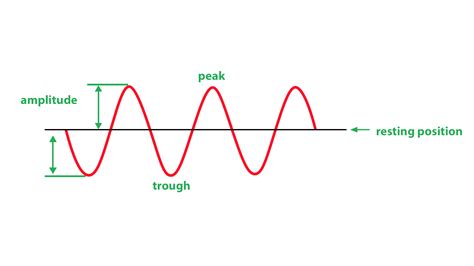
Frequency refers to the number of occurrences or cycles of a repetitive event in a given time interval. It is typically measured in Hertz (Hz), which represents one cycle per second. However, frequency can also be expressed in other units, such as kilohertz (kHz), megahertz (MHz), or gigahertz (GHz), depending on the range of values involved.
The concept of frequency is closely related to the idea of periodicity. A periodic event or signal is one that repeats itself in a regular and predictable manner. For example, the oscillation of a pendulum or the vibration of a guitar string are periodic events. The frequency of such events is determined by the time it takes for one complete cycle to occur.
Calculating Frequency
To calculate the frequency of a periodic event, we can use the following formula:
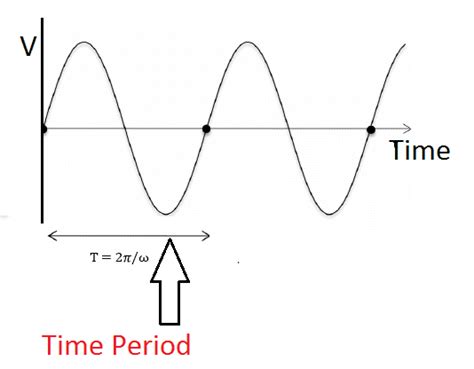
Frequency (f) = 1 / Period (T)
Where:
- f represents the frequency in Hz.
- T represents the period, which is the time taken for one complete cycle.
For example, if a pendulum completes one full swing (from one extreme position to the other and back) in 2 seconds, its period is 2 seconds. Using the formula, we can calculate its frequency as follows:
Frequency = 1 / 2 seconds = 0.5 Hz
This means the pendulum oscillates at a frequency of 0.5 Hz, or half a cycle per second.
Measuring Frequency
Frequency measurement is essential in various scientific and engineering disciplines. There are several methods and instruments used to measure frequency accurately:
1. Oscilloscopes
Oscilloscopes are electronic devices that display and analyze voltage signals over time. They can measure the frequency of electrical signals by analyzing the waveforms. Oscilloscopes are commonly used in electronics and telecommunications to troubleshoot and diagnose issues.
2. Frequency Counters
Frequency counters, also known as frequency meters, are devices specifically designed to measure frequency. They work by counting the number of cycles of a signal within a given time interval and then calculating the frequency. Frequency counters are highly accurate and are used in a wide range of applications, including radio frequency (RF) measurements.
3. Spectrum Analyzers
Spectrum analyzers are instruments that provide a visual representation of the frequency spectrum of a signal. They can measure the amplitude of different frequency components within a signal, allowing for the analysis of complex waveforms. Spectrum analyzers are widely used in audio and radio frequency engineering.
4. Time-Domain Analysis
In some cases, frequency can be determined through time-domain analysis. By measuring the time between consecutive events or cycles, the period can be calculated, and subsequently, the frequency can be derived using the formula mentioned earlier.
Applications of Frequency Measurement
Frequency measurement has numerous applications across various fields. Here are some key areas where frequency plays a vital role:
1. Acoustics and Audio
In the field of acoustics, frequency is used to describe the pitch of sound waves. The human ear can perceive a wide range of frequencies, and understanding frequency helps in audio engineering, music production, and speech recognition.
2. Electronics and Telecommunications
Frequency is a critical parameter in electronics and telecommunications. It is used to design and analyze circuits, determine the bandwidth of communication channels, and ensure proper signal transmission. Frequency measurement is essential for troubleshooting electronic devices and optimizing communication systems.
3. Radio Frequency (RF) Engineering
RF engineering involves the design and analysis of systems that use radio waves for communication and broadcasting. Frequency measurement is crucial in this field to ensure proper signal propagation, minimize interference, and allocate frequency bands efficiently.
4. Vibration Analysis
In mechanical systems, vibration analysis is essential for maintaining equipment and detecting potential issues. Frequency measurement is used to identify the natural frequencies of vibrating structures, which can help diagnose problems and improve system performance.
5. Optics and Lasers
Frequency is also relevant in optics and laser technology. Lasers produce light with a specific frequency, and understanding frequency allows for precise control and manipulation of laser beams.
Conclusion
Frequency is a fundamental concept that underpins many scientific and engineering disciplines. Its measurement and understanding are crucial for analyzing and manipulating signals, waves, and oscillations. From acoustics to electronics and telecommunications, frequency plays a vital role in shaping the world around us. By accurately measuring frequency, we can unlock the secrets of periodic events and leverage this knowledge to enhance our technological capabilities.
What is the difference between frequency and period?
+Frequency and period are reciprocal concepts. Frequency measures the number of cycles per unit time, while period measures the time taken for one complete cycle. The relationship between frequency (f) and period (T) is given by the formula: f = 1/T. In simpler terms, frequency tells us how often something happens, while period tells us how long it takes for one occurrence.
Can frequency be negative?
+No, frequency cannot be negative. Frequency is always a positive value, as it represents the number of occurrences or cycles in a positive time interval. However, it’s important to note that the phase of a wave can be negative, indicating a shift in the wave’s position relative to a reference point.
How is frequency related to wavelength in wave theory?
+In wave theory, frequency and wavelength are inversely proportional. The relationship between frequency (f), wavelength (λ), and wave speed (v) is given by the equation: v = fλ. This means that as frequency increases, wavelength decreases, and vice versa. For example, in the electromagnetic spectrum, higher frequencies correspond to shorter wavelengths, such as gamma rays, while lower frequencies correspond to longer wavelengths, like radio waves.
What are some common frequency ranges in different fields?
+Frequency ranges vary across different fields. Here are some common frequency ranges:
- Audio: 20 Hz to 20 kHz (human hearing range)
- Radio: 3 kHz to 300 GHz (used for radio broadcasting and communication)
- Microwaves: 300 MHz to 300 GHz (used in radar and microwave ovens)
- Infrared: 300 GHz to 400 THz (used in remote controls and thermal imaging)
- Visible Light: 400 THz to 790 THz (colors we can see)
How is frequency used in music and musical instruments?
+Frequency is a fundamental concept in music and musical instruments. Different musical notes correspond to specific frequencies. For example, the A4 note has a frequency of 440 Hz. Musical instruments produce sound by creating vibrations at specific frequencies, and understanding frequency helps musicians tune their instruments and create harmonious melodies.



